zerohertzLib.vision¶
Vision
다양한 image들을 handling하고 시각화하는 함수 및 class들
Important
Bbox의 types
cwh:[cx, cy, w, h]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])xyxy:[x0, y0, x1, y1]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])poly:[[x0, y0], [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]]로 구성된 bbox ([4, 2]or[N, 4, 2])
- class zerohertzLib.vision.CocoLoader(data_path, vis_path=None, class_color=None)[source]¶
Bases:
objectCOCO format의 dataset을 읽고 시각화하는 class
- Parameters:
- __call__()[source]¶
Index에 따른 image와 annotation에 대한 정보 return (
vis_path와class_color입력 시 시각화 imagevis_path에 저장)- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 indexread (
Optional[bool]) – Image 읽음 여부int_class (
Optional[bool]) – 출력될 class의 type 지정
- Returns:
Image 경로 혹은 읽어온 image와 그에 따른
class_list,bboxes,polys- Return type:
Tuple[Union[str, NDArray[np.uint8]], List[Union[int, str]], NDArray[DTypeLike], List[NDArray[DTypeLike]]]
- __getitem__()[source]¶
Index에 따른 image와 annotation에 대한 정보 return (
vis_path와class_color입력 시 시각화 imagevis_path에 저장)- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 index- Returns:
읽어온 image와 그에 따른
class_list,bboxes,polys- Return type:
Tuple[NDArray[np.uint8], List[str], NDArray[DTypeLike], List[NDArray[DTypeLike]]]
Examples
>>> data_path = "train" >>> class_color = {"label1": (0, 255, 0), "label2": (255, 0, 0)} >>> coco = zz.vision.CocoLoader(data_path, vis_path="tmp", class_color=class_color) >>> image, class_list, bboxes, polys = coco(0, False, True) >>> type(image) <class 'str'> >>> image '{IMAGE_PATH}.jpg' >>> class_list [0, 1] >>> type(bboxes) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> >>> bboxes.shape (2, 4) >>> image, class_list, bboxes, polys = coco[0] >>> type(image) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> >>> class_list ['label1', 'label2'] >>> type(bboxes) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> >>> bboxes.shape (2, 4) >>> type(polys) <class 'list'>
- yolo(target_path, label=None, poly=False)[source]¶
COCO format을 YOLO format으로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{target_path}/images및{target_path}/labels에 image와 .txt file 저장- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> coco = zz.vision.CocoLoader(data_path) >>> coco.yolo(target_path) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s] >>> label = ["label1", "label2"] >>> cooc.yolo(target_path, label) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
- class zerohertzLib.vision.ImageLoader(path='./', cnt=1)[source]¶
Bases:
object경로와 image의 수를 지정하여 경로 내 image를 return하는 class
- image_paths¶
지정한 경로 내 image들의 경로
- Type:
List[str]
- __getitem__()[source]¶
- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 index- Returns:
cnt에 따른 file 경로 및 image 값- Return type:
Union[Tuple[str, NDArray[np.uint8]], Tuple[List[str], List[NDArray[np.uint8]]]
Examples
>>> il = zz.vision.ImageLoader() >>> len(il) 510 >>> il[0][0] './1.2.410.200001.1.9999.1.20220513101953581.1.1.jpg' >>> il[0][1].shape (480, 640, 3) >>> il = zz.vision.ImageLoader(cnt=4) >>> len(il) 128 >>> il[0][0] ['./1.2.410.200001.1.9999.1.20220513101953581.1.1.jpg', '...', '...', '...'] >>> il[0][1][0].shape (480, 640, 3) >>> len(il[0][0]) 4 >>> len(il[0][1]) 4
- class zerohertzLib.vision.JsonImageLoader(data_path, json_path, json_key)[source]¶
Bases:
objectJSON file을 통해 image와 JSON file 내 정보를 불러오는 class
- Parameters:
- json¶
JSON file들을 읽어 data 구축 시 활용
- Type:
zerohertzLib.util.JsonDir
- __getitem__()[source]¶
읽어온 JSON file들을 list와 같이 indexing 후 해당하는 image return
- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 index- Returns:
Image와 JSON 내 정보
- Return type:
Tuple[NDArray[np.uint8], zerohertzLib.util.Json]
Examples
>>> jil = zz.vision.JsonImageLoader(data_path, json_path, json_key) 100%|█████████████| 17248/17248 [00:04<00:00, 3581.22it/s] >>> img, js = jil[10] >>> img.shape (600, 800, 3) >>> js.tree() └─ info └─ name └─ date_created ...
- class zerohertzLib.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path=None)[source]¶
Bases:
objectLabel Studio 관련 data를 handling하는 class
- Parameters:
- __getitem__()[source]¶
- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 index- Returns:
Index에 따른 image file 이름 또는 경로와 JSON file에 포함될 dictionary 또는 annotation 정보
- Return type:
Union[Tuple[str, Dict[str, Dict[str, str]]], Tuple[str, Dict[str, List[Any]]]]
Examples
- Without
json_path: >>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path) >>> ls[0] ('0000007864.png', {'data': {'image': 'data/local-files/?d=/label-studio/data/local/tmp/0000007864.png'}}) >>> ls[1] ('0000008658.png', {'data': {'image': 'data/local-files/?d=/label-studio/data/local/tmp/0000008658.png'}})
- With
json_path: - Bbox:
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> ls[0] >>> ls[0] ('/PATH/TO/IMAGE', {'labels': ['label1', ...], 'polys': [array([0.39471694, 0.30683403, 0.03749811, 0.0167364 ]), ...], 'whs': [(1660, 2349), ...]}) >>> ls[1] ('/PATH/TO/IMAGE', {'labels': ['label2', ...], 'polys': [array([0.29239837, 0.30149896, 0.04013469, 0.02736506]), ...], 'whs': [(1655, 2324), ...]}) >>> ls.labels {'label1', 'label2'} >>> ls.type 'rectanglelabels'
- Poly:
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> ls[0] ('/PATH/TO/IMAGE', {'labels': ['label1', ...], 'polys': [array([[0.4531892 , 0.32880674], ..., [0.46119428, 0.32580483]]), ...], 'whs': [(3024, 4032), ...]}) >>> ls[1] ('/PATH/TO/IMAGE', {'labels': ['label2', ...], 'polys': [array([[0.31973699, 0.14660367], ..., [0.29032053, 0.1484422 ]]), ...], 'whs': [(3024, 4032), ...]}) >>> ls.labels {'label1', 'label2'} >>> ls.type 'polygonlabels'
- classification(target_path, label=None, rand=0, shrink=True, aug=1)[source]¶
Label Studio로 annotation한 JSON data를 classification format으로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{target_path}/{label}/{img_file_name}_{idx}_{i}.{img_file_ext}에 image 저장 (idx: annotation의 index,i:rand의 index)- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> ls.classification(target_path) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s] >>> label = {"label1": "lab1", "label2": "lab2"} >>> ls.classification(target_path, label, rand=10, aug=10, shrink=False) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
- coco(target_path, label)[source]¶
Label Studio로 annotation한 JSON data를 COCO format으로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{target_path}.json에 JSON file 저장- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> label = {"label1": 1, "label2": 2} >>> ls.coco(target_path, label) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
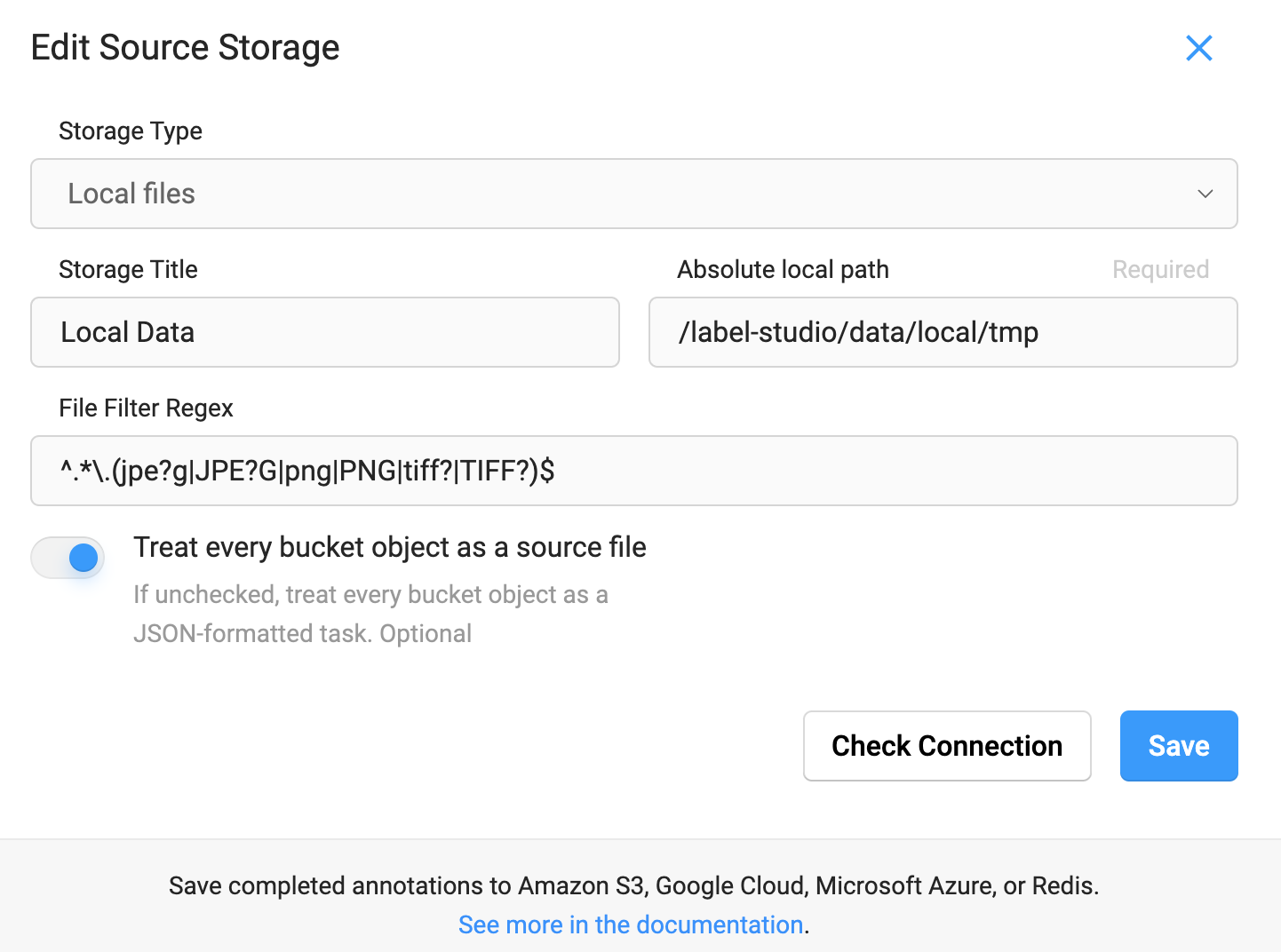
- json(path='/label-studio/data/local', data_function=None)[source]¶
Label Studio에 mount된 data를 불러오기 위한 JSON file 생성
Note
아래와 같이 환경 변수가 설정된 Label Studio image를 사용하면
LabelStudioclass로 생성된 JSON file을 적용할 수 있다.FROM heartexlabs/label-studio ENV LABEL_STUDIO_LOCAL_FILES_SERVING_ENABLED=true
docker run --name label-studio -p 8080:8080 -v ${PWD}/data:/label-studio/data label-studio
Projects→{PROJECT_NAME}→Settings→Cloud Storage→Add Source Storage클릭 후 아래와 같이 정보를 기재하고Sync Storage를 누른다.Storage Type:
Local filesAbsolute local path:
/label-studio/data/local/${PATH}(data_path:${PWD}/data/local)File Filter Regex:
^.*\.(jpe?g|JPE?G|png|PNG|tiff?|TIFF?)$Treat every bucket object as a source file:
True
Sync 이후
LabelStudioclass로 생성된 JSON file을 Label Studio에 import하면 아래와 같이 setup 할 수 있다.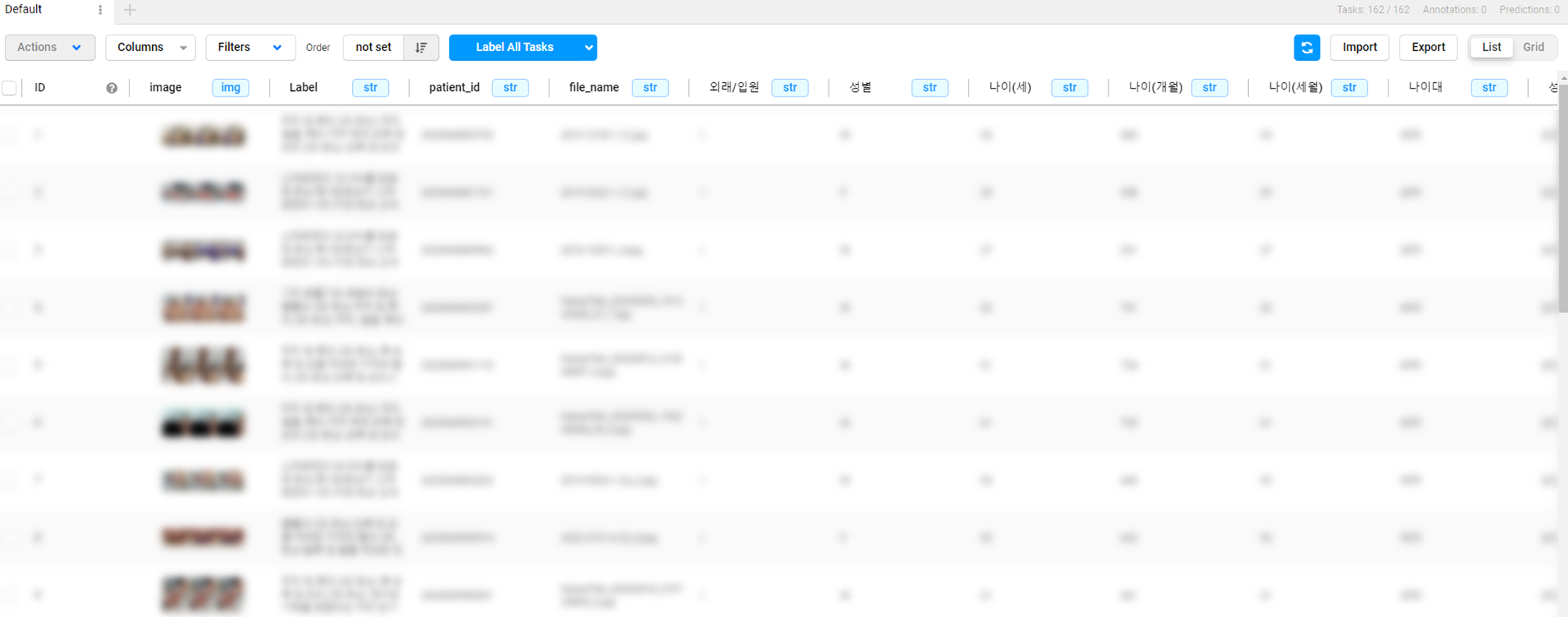
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{data_path}.json에 결과 저장- Return type:
None
Examples
- Default:
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path) >>> ls.json() 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 259993.32it/s
[ { "data": { "image": "data/local-files/?d=/label-studio/data/local/tmp/0000007864.png" } }, { "data": { "...": "..." } }, ]
- With
data_function: def data_function(file_name): return data_store[file_name]
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path) >>> ls.json(data_function) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
[ { "data": { "image": "data/local-files/?d=/label-studio/data/local/tmp/0000007864.png", "Label": "...", "patient_id": "...", "...": "...", } }, { "data": { "...": "..." } }, ]
- labelme(target_path, label=None)[source]¶
Label Studio로 annotation한 JSON data를 LabelMe format으로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{target_path}/images및{target_path}/labels에 image와 JSON file 저장- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> ls.labelme(target_path) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s] >>> label = {"label1": "lab1", "label2": "lab2"} >>> ls.labelme(target_path, label) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
- yolo(target_path, label=None)[source]¶
Label Studio로 annotation한 JSON data를 YOLO format으로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
{target_path}/images및{target_path}/labels에 image와 .txt file 저장- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> ls = zz.vision.LabelStudio(data_path, json_path) >>> ls.yolo(target_path) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s] >>> label = ["label1", "label2"] >>> ls.yolo(target_path, label) 100%|█████████████| 476/476 [00:00<00:00, 78794.25it/s]
- class zerohertzLib.vision.YoloLoader(data_path='images', txt_path='labels', poly=False, absolute=False, vis_path=None, class_color=None)[source]¶
Bases:
objectYOLO format의 dataset을 읽고 시각화하는 class
- Parameters:
data_path¶ (
Optional[str]) – Image가 존재하는 directory 경로txt_path¶ (
Optional[str]) – YOLO format의.txt가 존재하는 directory 경로poly¶ (
Optional[bool]) –.txtfile의 format (False: detection,True: segmentation)absolute¶ (
Optional[bool]) –.txtfile의 절대 좌표계 여부 (False: relative coordinates,True: absolute coordinates)vis_path¶ (
Optional[str]) – 시각화 image들이 저장될 경로class_color¶ (
Optional[Dict[Union[int, str], Tuple[int]]]) – 시각화 결과에 적용될 class에 따른 색상
- __getitem__()[source]¶
Index에 따른 image와
.txtfile에 대한 정보 return (vis_path와class_color입력 시 시각화 imagevis_path에 저장)- Parameters:
idx (
int) – 입력 index- Returns:
읽어온 image와 그에 따른
class_list및bbox혹은poly- Return type:
Tuple[NDArray[np.uint8], List[int], List[NDArray[DTypeLike]]]
Examples
>>> data_path = ".../images" >>> txt_path = ".../labels" >>> class_color = {0: (0, 255, 0), 1: (255, 0, 0), 2: (0, 0, 255)} >>> yolo = zz.vision.YoloLoader(data_path, txt_path, poly=True, absolute=False, vis_path="tmp", class_color=class_color) >>> image, class_list, objects = yolo[0] >>> type(image) <class 'numpy.ndarray'> >>> class_list [1, 1] >>> len(objects) 2
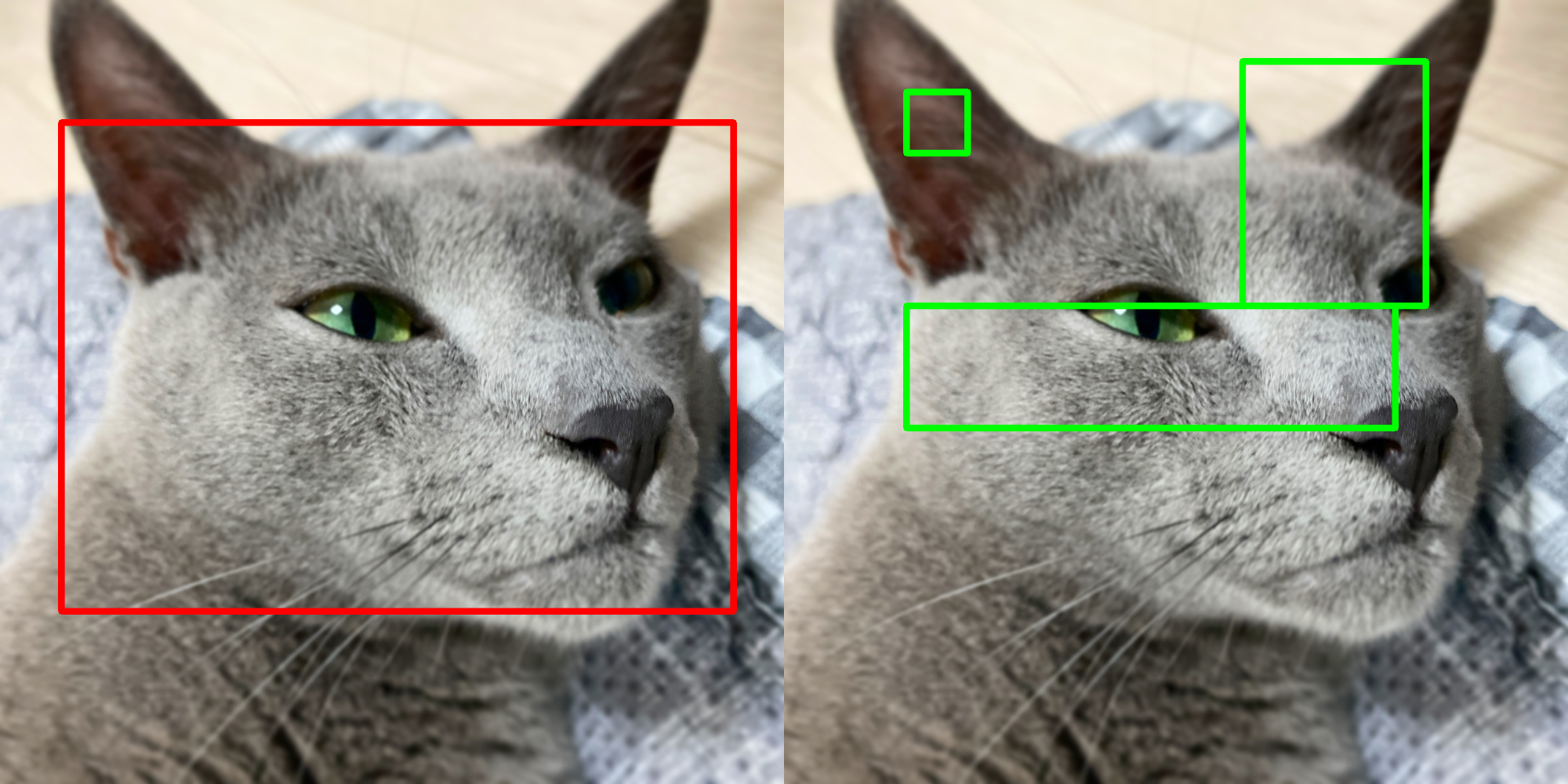
- zerohertzLib.vision.bbox(img, box, color=(0, 0, 255), thickness=2)[source]¶
여러 Bbox 시각화
- Parameters:
- Returns:
시각화 결과 (
[H, W, C])- Return type:
NDArray[np.uint8]
Examples
- Bbox:
>>> box = np.array([[100, 200], [100, 1000], [1200, 1000], [1200, 200]]) >>> box.shape (4, 2) >>> res1 = zz.vision.bbox(img, box, thickness=10)
- Bboxes:
>>> boxes = np.array([[250, 200, 100, 100], [600, 600, 800, 200], [900, 300, 300, 400]]) >>> boxes.shape (3, 4) >>> res2 = zz.vision.bbox(img, boxes, (0, 255, 0), thickness=10)
- zerohertzLib.vision.before_after(before, after, area=None, per=True, quality=100, file_name='tmp')[source]¶
두 image를 비교하는 image 생성
- Parameters:
- Returns:
현재 directory에 바로 image 저장
- Return type:
None
Examples
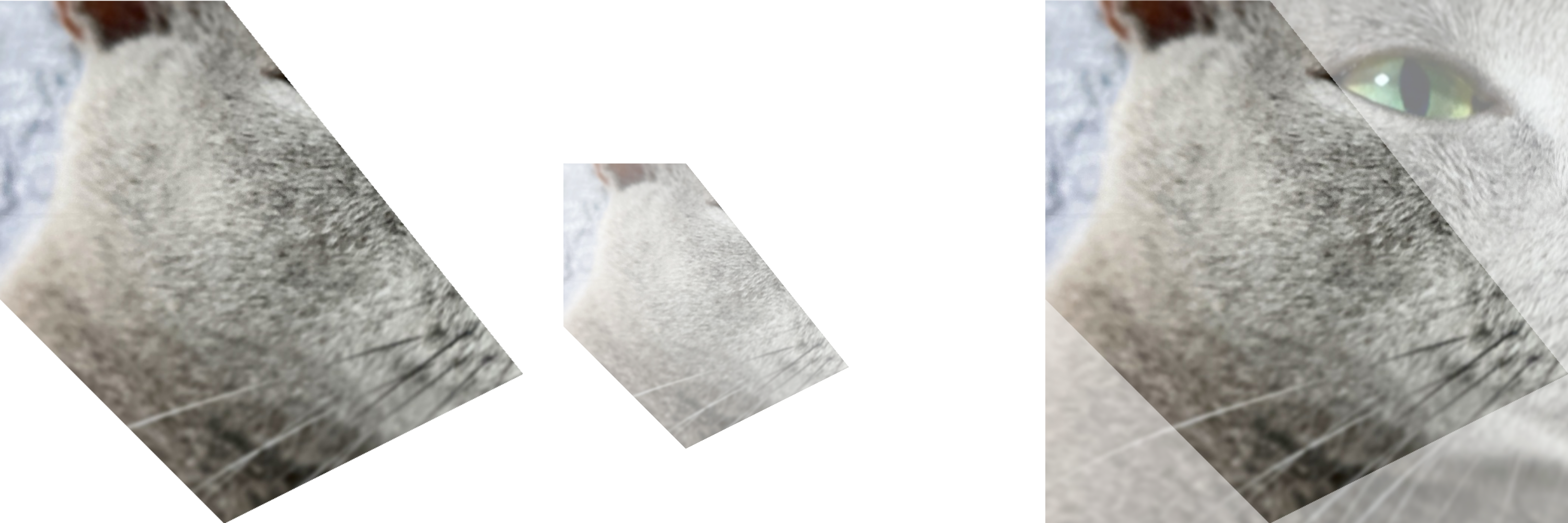
- zerohertzLib.vision.cutout(img, poly, alpha=255, crop=True, background=0)[source]¶
Image 내에서 지정한 좌표를 제외한 부분을 투명화
- Parameters:
- Returns:
출력 image (
[H, W, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[np.uint8]
Examples
>>> poly = np.array([[100, 400], [400, 400], [800, 900], [400, 1100], [100, 800]]) >>> res1 = zz.vision.cutout(img, poly) >>> res2 = zz.vision.cutout(img, poly, 128, False) >>> res3 = zz.vision.cutout(img, poly, background=128)

- zerohertzLib.vision.cwh2poly(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[cx, cy, w, h]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Returns:
[[x0, y0], [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]]로 구성된 bbox ([4, 2]or[N, 4, 2])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.cwh2poly([20, 30, 20, 20]) array([[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]]) >>> zz.vision.cwh2poly(np.array([[20, 30, 20, 20], [50, 75, 40, 50]])) array([[[ 10, 20], [ 30, 20], [ 30, 40], [ 10, 40]], [[ 30, 50], [ 70, 50], [ 70, 100], [ 30, 100]]])
- zerohertzLib.vision.cwh2xyxy(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[cx, cy, w, h]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Returns:
[x0, y0, x1, y1]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.cwh2xyxy([20, 30, 20, 20]) array([10, 20, 30, 40]) >>> zz.vision.cwh2xyxy(np.array([[20, 30, 20, 20], [50, 75, 40, 50]])) array([[ 10, 20, 30, 40], [ 30, 50, 70, 100]])
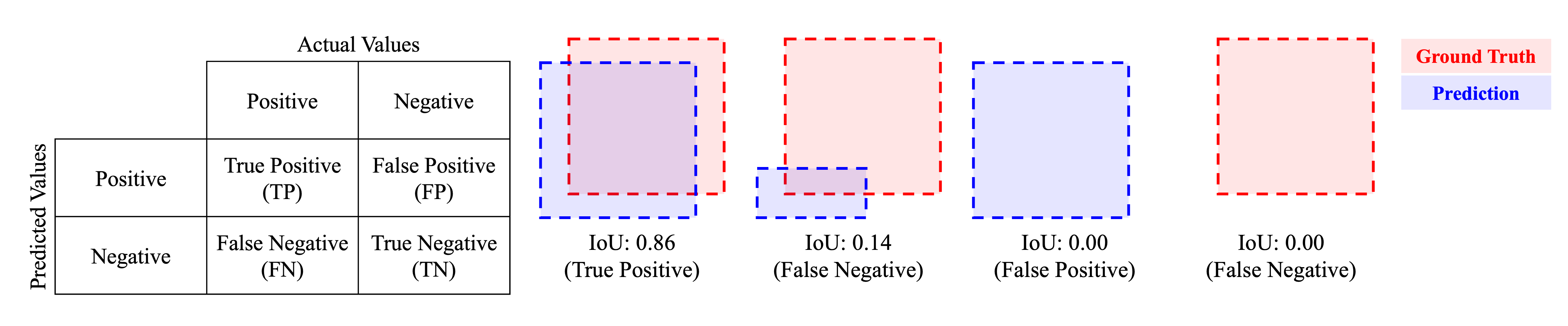
- zerohertzLib.vision.evaluation(ground_truths, inferences, confidences, gt_classes=None, inf_classes=None, file_name=None, threshold=0.5)[source]¶
단일 이미지 내 detection model의 추론 성능 평가
- Parameters:
ground_truths¶ (
NDArray[DTypeLike]) – Ground truth object들의 polygon ([N, 4, 2],[[[x_0, y_0], [x_1, y_1], ...], ...])inferences¶ (
NDArray[DTypeLike]) – Model이 추론한 각 object들의 polygon ([M, 4, 2],[[[x_0, y_0], [x_1, y_1], ...], ...])confidences¶ (
List[float]) – Model이 추론한 각 object들의 confidence([M])gt_classes¶ (
Optional[List[str]]) – Ground truth object들의 class ([N])inf_classes¶ (
Optional[List[str]]) – Model이 추론한 각 object들의 class ([M])file_name¶ (
Optional[str]) – 평가 image의 이름threshold¶ (
Optional[float]) – IoU의 threshold
- Returns:
단일 이미지의 model 성능 평가 결과
- Return type:
pd.DataFrame
Examples
>>> poly = np.array([[0, 0], [10, 0], [10, 10], [0, 10]]) >>> ground_truths = np.array([poly, poly + 20, poly + 40]) >>> inferences = np.array([poly, poly + 19, poly + 80]) >>> confidences = np.array([0.6, 0.7, 0.8]) >>> zz.vision.evaluation(ground_truths, inferences, confidences, file_name="test.png") file_name instance confidence class IoU results gt_x0 gt_y0 gt_x1 gt_y1 gt_x2 gt_y2 gt_x3 gt_y3 inf_x0 inf_y0 inf_x1 inf_y1 inf_x2 inf_y2 inf_x3 inf_y3 0 test.png 0 0.8 0.0 0.000000 FP NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN 80.0 80.0 90.0 80.0 90.0 90.0 80.0 90.0 1 test.png 1 0.7 0.0 0.680672 TP 20.0 20.0 30.0 20.0 30.0 30.0 20.0 30.0 19.0 19.0 29.0 19.0 29.0 29.0 19.0 29.0 2 test.png 2 0.6 0.0 1.000000 TP 0.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 3 test.png 3 0.0 0.0 0.000000 FN 40.0 40.0 50.0 40.0 50.0 50.0 40.0 50.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN >>> gt_classes = np.array(["cat", "dog", "cat"]) >>> inf_classes = np.array(["cat", "dog", "cat"]) >>> zz.vision.evaluation(ground_truths, inferences, confidences, gt_classes, inf_classes) instance confidence class IoU results gt_x0 gt_y0 gt_x1 gt_y1 gt_x2 gt_y2 gt_x3 gt_y3 inf_x0 inf_y0 inf_x1 inf_y1 inf_x2 inf_y2 inf_x3 inf_y3 0 0 0.8 cat 0.000000 FP NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN 80.0 80.0 90.0 80.0 90.0 90.0 80.0 90.0 1 1 0.6 cat 1.000000 TP 0.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 0.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 10.0 0.0 10.0 2 2 0.0 cat 0.000000 FN 40.0 40.0 50.0 40.0 50.0 50.0 40.0 50.0 NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN NaN 3 3 0.7 dog 0.680672 TP 20.0 20.0 30.0 20.0 30.0 30.0 20.0 30.0 19.0 19.0 29.0 19.0 29.0 29.0 19.0 29.0
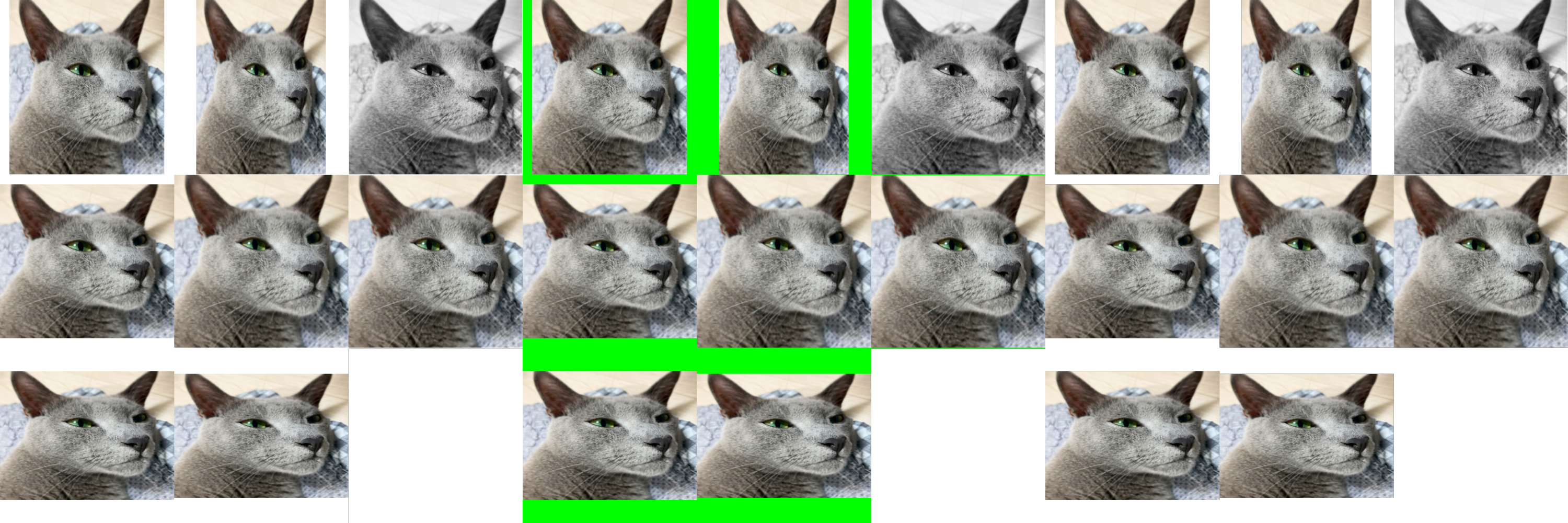
- zerohertzLib.vision.grid(imgs, size=1000, color=(255, 255, 255), file_name='tmp')[source]¶
여러 image를 입력받아 정방형 image로 병합
- Parameters:
- Returns:
현재 directory에 바로 image 저장
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> imgs = [cv2.resize(img, (random.randrange(300, 1000), random.randrange(300, 1000))) for _ in range(8)] >>> imgs[2] = cv2.cvtColor(imgs[2], cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY) >>> imgs[3] = cv2.cvtColor(imgs[3], cv2.COLOR_BGR2BGRA) >>> zz.vision.grid(imgs) >>> zz.vision.grid(imgs, color=(0, 255, 0)) >>> zz.vision.grid(imgs, color=(0, 0, 0, 0))

- zerohertzLib.vision.img2gif(path, file_name='tmp', duration=500)[source]¶
Directory 내 image들을 GIF로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
현재 directory에 바로 GIF 저장
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> zz.vision.img2gif("./")

- zerohertzLib.vision.iou(poly1, poly2)[source]¶
IoU (Intersection over Union)를 계산하는 함수
- Parameters:
- Returns:
IoU 값
- Return type:
float
Examples
>>> poly1 = np.array([[0, 0], [10, 0], [10, 10], [0, 10]]) >>> poly2 = poly1 + (5, 0) >>> poly2 array([[ 5, 0], [15, 0], [15, 10], [ 5, 10]]) >>> zz.vision.iou(poly1, poly2) 0.3333333333333333
- zerohertzLib.vision.is_pts_in_poly(poly, pts)[source]¶
지점들의 좌표 내 존재 여부 확인 함수
- Parameters:
- Returns:
입력
point의 다각형poly내부 존재 여부- Return type:
Union[bool, NDArray[bool]]
Examples
>>> poly = np.array([[10, 10], [20, 10], [30, 40], [20, 60], [10, 20]]) >>> zz.vision.is_pts_in_poly(poly, [20, 20]) True >>> zz.vision.is_pts_in_poly(poly, [[20, 20], [100, 100]]) array([ True, False]) >>> zz.vision.is_pts_in_poly(poly, np.array([20, 20])) True >>> zz.vision.is_pts_in_poly(poly, np.array([[20, 20], [100, 100]])) array([ True, False])
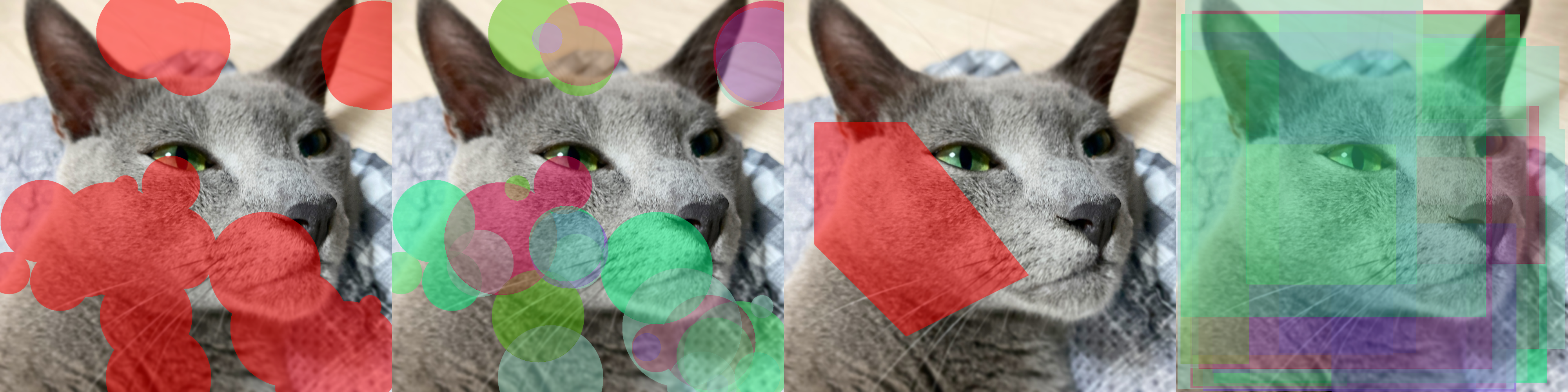
- zerohertzLib.vision.mask(img, mks=None, poly=None, color=(0, 0, 255), class_list=None, class_color=None, border=True, alpha=0.5)[source]¶
Mask 시각화
- Parameters:
img¶ (
NDArray[np.uint8]) – 입력 image ([H, W, C])mks¶ (
Optional[NDArray[bool]]) – 입력 image 위에 병합할 mask ([H, W]or[N, H, W])poly¶ (
Optional[Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike], List[NDArray[DTypeLike]]]]) – 입력 image 위에 병합할 mask ([M, 2]or[N, M, 2])color¶ (
Optional[Tuple[int]]) – Mask의 색class_list¶ (
Optional[List[Union[int, str]]]) –mks의 index에 따른 classclass_color¶ (
Optional[Dict[Union[int, str], Tuple[int]]]) – Class에 따른 색 (color무시)border¶ (
Optional[bool]) – Mask의 경계선 표시 여부alpha¶ (
Optional[float]) – Mask의 투명도
- Returns:
시각화 결과 (
[H, W, C])- Return type:
NDArray[np.uint8]
Examples
- Mask (without class):
>>> H, W, _ = img.shape >>> cnt = 30 >>> mks = np.zeros((cnt, H, W), np.uint8) >>> for mks_ in mks: >>> center_x = random.randint(0, W) >>> center_y = random.randint(0, H) >>> radius = random.randint(30, 200) >>> cv2.circle(mks_, (center_x, center_y), radius, (True), -1) >>> mks = mks.astype(bool) >>> res1 = zz.vision.mask(img, mks)
- Mask (with class):
>>> cls = [i for i in range(cnt)] >>> class_list = [cls[random.randint(0, 5)] for _ in range(cnt)] >>> class_color = {} >>> for c in cls: >>> class_color[c] = [random.randint(0, 255) for _ in range(3)] >>> res2 = zz.vision.mask(img, mks, class_list=class_list, class_color=class_color)
- Poly (without class):
>>> poly = np.array([[100, 400], [400, 400], [800, 900], [400, 1100], [100, 800]]) >>> res3 = zz.vision.mask(img, poly=poly)
- Poly (with class):
>>> poly = zz.vision.xyxy2poly(zz.vision.poly2xyxy((np.random.rand(cnt, 4, 2) * (W, H)))) >>> res4 = zz.vision.mask(img, poly=poly, class_list=class_list, class_color=class_color)
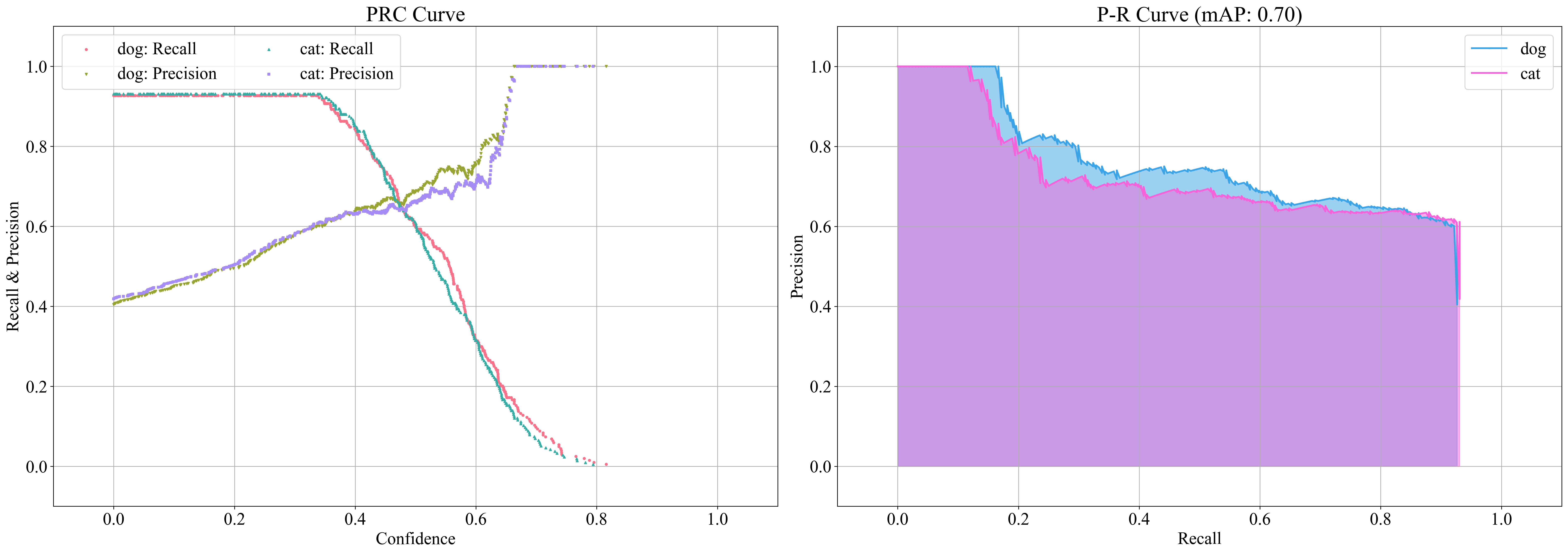
- zerohertzLib.vision.meanap(logs)[source]¶
Detection model의 P-R curve 시각화 및 mAP 산출
- Parameters:
logs¶ (
pd.DataFrame) –zz.vision.evaluation함수를 통해 평가된 결과- Returns:
mAP 값 및 class에 따른 AP 값 (시각화 결과는
prc_curve.png,pr_curve.png로 현재 directory에 저장)- Return type:
Tuple[float, Dict[str, float]]
Examples
>>> logs1 = zz.vision.evaluation(ground_truths_1, inferences_1, confidences_1, gt_classes, inf_classes, file_name="test_1.png") >>> logs2 = zz.vision.evaluation(ground_truths_2, inferences_2, confidences_2, gt_classes, inf_classes, file_name="test_2.png") >>> logs = pd.concat([logs1, logs2], ignore_index=True) >>> zz.vision.meanap(logs) (0.7030629916206652, defaultdict(<class 'float'>, {'dog': 0.7177078883735305, 'cat': 0.6884180948677999}))
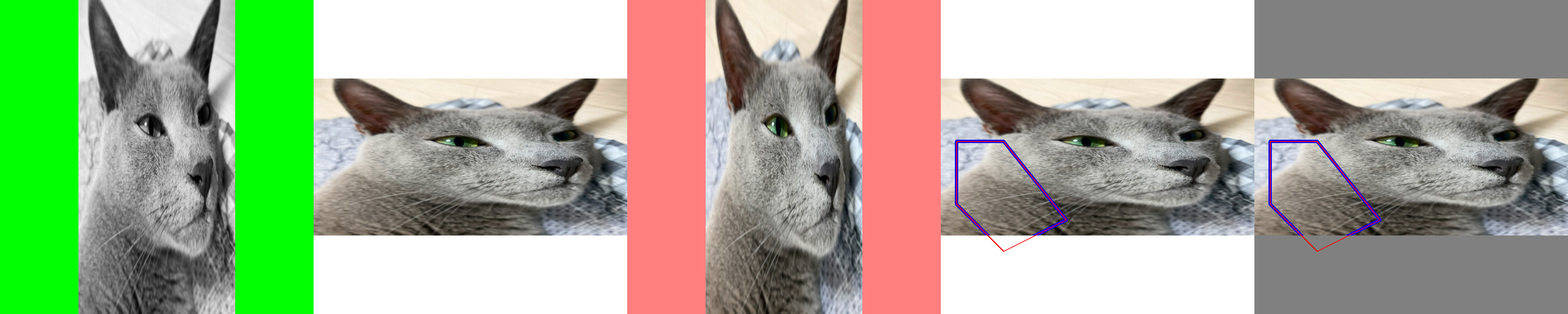
- zerohertzLib.vision.pad(img, shape, color=(255, 255, 255), poly=None)[source]¶
입력 image를 원하는 shape로 resize 및 pad
- Parameters:
- Returns:
출력 image (
[H, W, C]) 및 padding에 따른 정보 또는 변형된 좌표값- Return type:
Tuple[NDArray[np.uint8], Union[Tuple[float, int, int], NDArray[DTypeLike]]]
Note
poly를 입력하지 않을 시(ratio, left, top)가 출력되며poly * ratio + (left, top)와 같이 차후에 변환 가능Examples
- GRAY:
>>> img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGRA2GRAY) >>> res1 = cv2.resize(img, (500, 1000)) >>> res1, _ = zz.vision.pad(res1, (1000, 1000), color=(0, 255, 0))
- BGR:
>>> res2 = cv2.resize(img, (1000, 500)) >>> res2, _ = zz.vision.pad(res2, (1000, 1000))
- BGRA:
>>> img = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2BGRA) >>> res3 = cv2.resize(img, (500, 1000)) >>> res3, _ = zz.vision.pad(res3, (1000, 1000), color=(0, 0, 255, 128))
- Poly:
>>> poly = np.array([[100, 400], [400, 400], [800, 900], [400, 1100], [100, 800]]) >>> res4 = cv2.resize(img, (2000, 1000)) >>> res4 = zz.vision.bbox(res4, poly, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=20) >>> res4, poly = zz.vision.pad(res4, (1000, 1000), poly=poly) >>> res4 = zz.vision.bbox(res4, poly, color=(0, 0, 255))
- Transformation:
>>> poly = np.array([[100, 400], [400, 400], [800, 900], [400, 1100], [100, 800]]) >>> res5 = cv2.resize(img, (2000, 1000)) >>> res5 = zz.vision.bbox(res5, poly, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=20) >>> res5, info = zz.vision.pad(res5, (1000, 1000), color=(128, 128, 128)) >>> poly = poly * info[0] + info[1:] >>> res5 = zz.vision.bbox(res5, poly, color=(0, 0, 255))

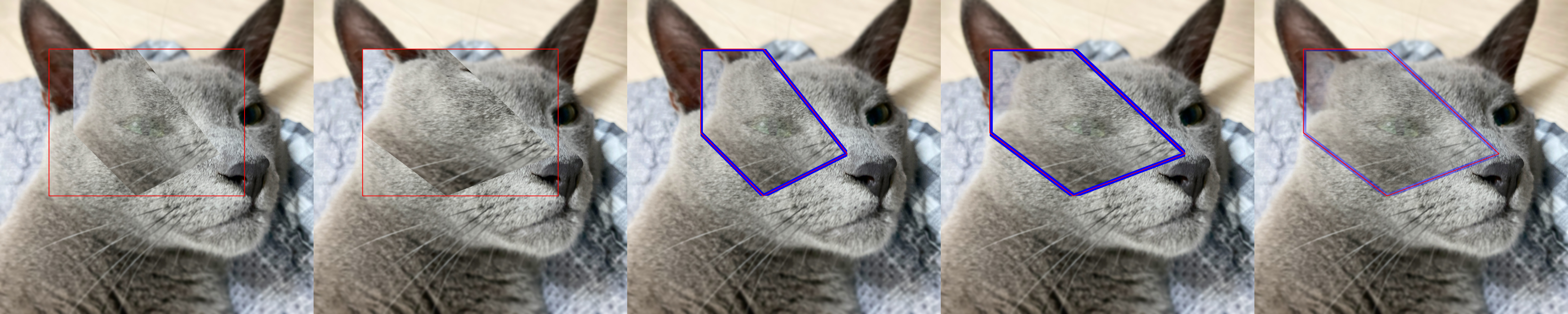
- zerohertzLib.vision.paste(img, target, box, resize=False, vis=False, poly=None, alpha=None, gaussian=None)[source]¶
targetimage를img위에 투명도를 포함하여 병합Note
PIL.Image.paste를numpy와cv2기반으로 구현>>> img = Image.open("test.png").convert("RGBA") >>> target = Image.open("target.png").convert("RGBA") >>> img.paste(target, (0, 0), target)
- Parameters:
img¶ (
NDArray[np.uint8]) – 입력 image ([H, W, C])target¶ (
NDArray[np.uint8]) – Target image ([H, W, 4])box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) – 병합될 영역 (xyxy형식)resize¶ (
Optional[bool]) – Target image의 resize 여부vis¶ (
Optional[bool]) – 지정한 영역 (box)의 시각화 여부poly¶ (
Optional[NDArray[DTypeLike]]) – 변형된 좌표 ([N, 2])alpha¶ (
Optional[int]) –targetimage의 투명도 변경gaussian¶ (
Optional[int]) – 자연스러운 병합을 위해target의 alpha channel에 적용될 Gaussian blur의 kernel size
- Returns:
시각화 결과 (
[H, W, 4]) 및poly입력 시 변형된 좌표값- Return type:
Union[NDArray[np.uint8], Tuple[NDArray[np.uint8], NDArray[DTypeLike]]]
Examples
- Without Poly:
>>> poly = np.array([[100, 400], [400, 400], [800, 900], [400, 1100], [100, 800]]) >>> target = zz.vision.cutout(img, poly, 200) >>> res1 = zz.vision.paste(img, target, [200, 200, 1000, 800], resize=False, vis=True) >>> res2 = zz.vision.paste(img, target, [200, 200, 1000, 800], resize=True, vis=True, alpha=255)
- With Poly:
>>> poly -= zz.vision.poly2xyxy(poly)[:2] >>> target = zz.vision.bbox(target, poly, color=(255, 0, 0), thickness=20) >>> res3, poly3 = zz.vision.paste(img, target, [200, 200, 1000, 800], resize=False, poly=poly) >>> poly3 array([[300. , 200. ], [557.14285714, 200. ], [900. , 628.57142857], [557.14285714, 800. ], [300. , 542.85714286]]) >>> res3 = zz.vision.bbox(res3, poly3) >>> res4, poly4 = zz.vision.paste(img, target, [200, 200, 1000, 800], resize=True, poly=poly) >>> poly4 array([[ 200. , 200. ], [ 542.85714286, 200. ], [1000. , 628.57142857], [ 542.85714286, 800. ], [ 200. , 542.85714286]]) >>> res4 = zz.vision.bbox(res4, poly4)
- Gaussian Blur:
>>> res5, poly5 = zz.vision.paste(img, target, [200, 200, 1000, 800], resize=True, poly=poly, gaussian=501) >>> res5 = zz.vision.bbox(res5, poly5)
- zerohertzLib.vision.poly2area(poly)[source]¶
다각형의 면적을 산출하는 함수
- Parameters:
poly¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) – 다각형 ([N, 2])- Returns:
다각형의 면적
- Return type:
float
Examples
>>> poly = [[10, 10], [20, 10], [30, 40], [20, 60], [10, 20]] >>> zz.vision.poly2area(poly) 550.0 >>> box = np.array([[100, 200], [1200, 200], [1200, 1000], [100, 1000]]) >>> zz.vision.poly2area(box) 880000.0
- zerohertzLib.vision.poly2cwh(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[[x0, y0], [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]]로 구성된 bbox ([4, 2]or[N, 4, 2])- Returns:
[cx, cy, w, h]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.poly2cwh([[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]]) array([20, 30, 20, 20]) >>> zz.vision.poly2cwh(np.array([[[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]], [[30, 50], [70, 50], [70, 100], [30, 100]]])) array([[20, 30, 20, 20], [50, 75, 40, 50]])
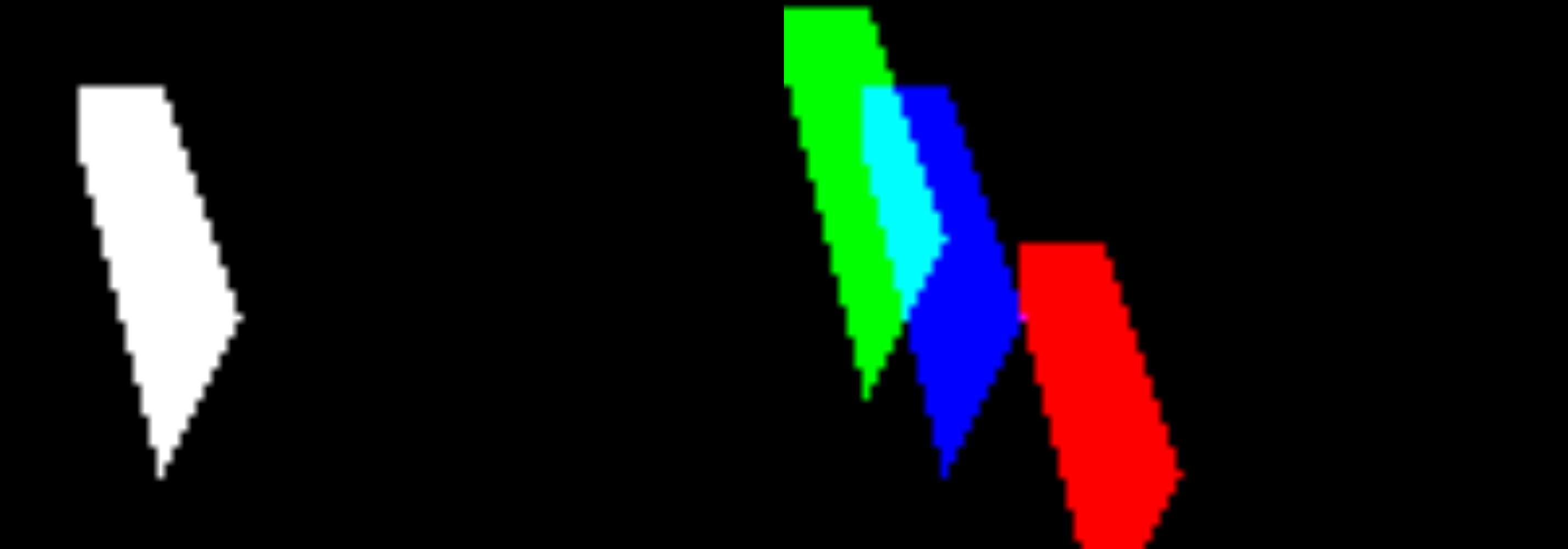
- zerohertzLib.vision.poly2mask(poly, shape)[source]¶
다각형 좌표를 입력받아 mask로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
변환된 mask (
[H, W]or[N, H, W])- Return type:
NDArray[bool]
Examples
>>> poly = [[10, 10], [20, 10], [30, 40], [20, 60], [10, 20]] >>> mask1 = zz.vision.poly2mask(poly, (70, 100)) >>> mask1.shape (70, 100) >>> mask1.dtype dtype('bool') >>> poly = np.array(poly) >>> mask2 = zz.vision.poly2mask([poly, poly - 10, poly + 20], (70, 100)) >>> mask2.shape (3, 70, 100) >>> mask2.dtype dtype('bool')
- zerohertzLib.vision.poly2ratio(poly)[source]¶
다각형의 bbox 대비 다각형의 면적 비율을 산출하는 함수
- Parameters:
poly¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) – 다각형 ([N, 2])- Returns:
다각형의 bbox 대비 다각형의 비율
- Return type:
float
Examples
>>> poly = [[10, 10], [20, 10], [30, 40], [20, 60], [10, 20]] >>> zz.vision.poly2ratio(poly) 0.55 >>> box = np.array([[100, 200], [1200, 200], [1200, 1000], [100, 1000]]) >>> zz.vision.poly2ratio(box) 1.0
- zerohertzLib.vision.poly2xyxy(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[[x0, y0], [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]]로 구성된 bbox ([4, 2]or[N, 4, 2])- Returns:
[x0, y0, x1, y1]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.poly2xyxy([[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]]) array([10, 20, 30, 40]) >>> zz.vision.poly2xyxy(np.array([[[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]], [[30, 50], [70, 50], [70, 100], [30, 100]]])) array([[ 10, 20, 30, 40], [ 30, 50, 70, 100]])
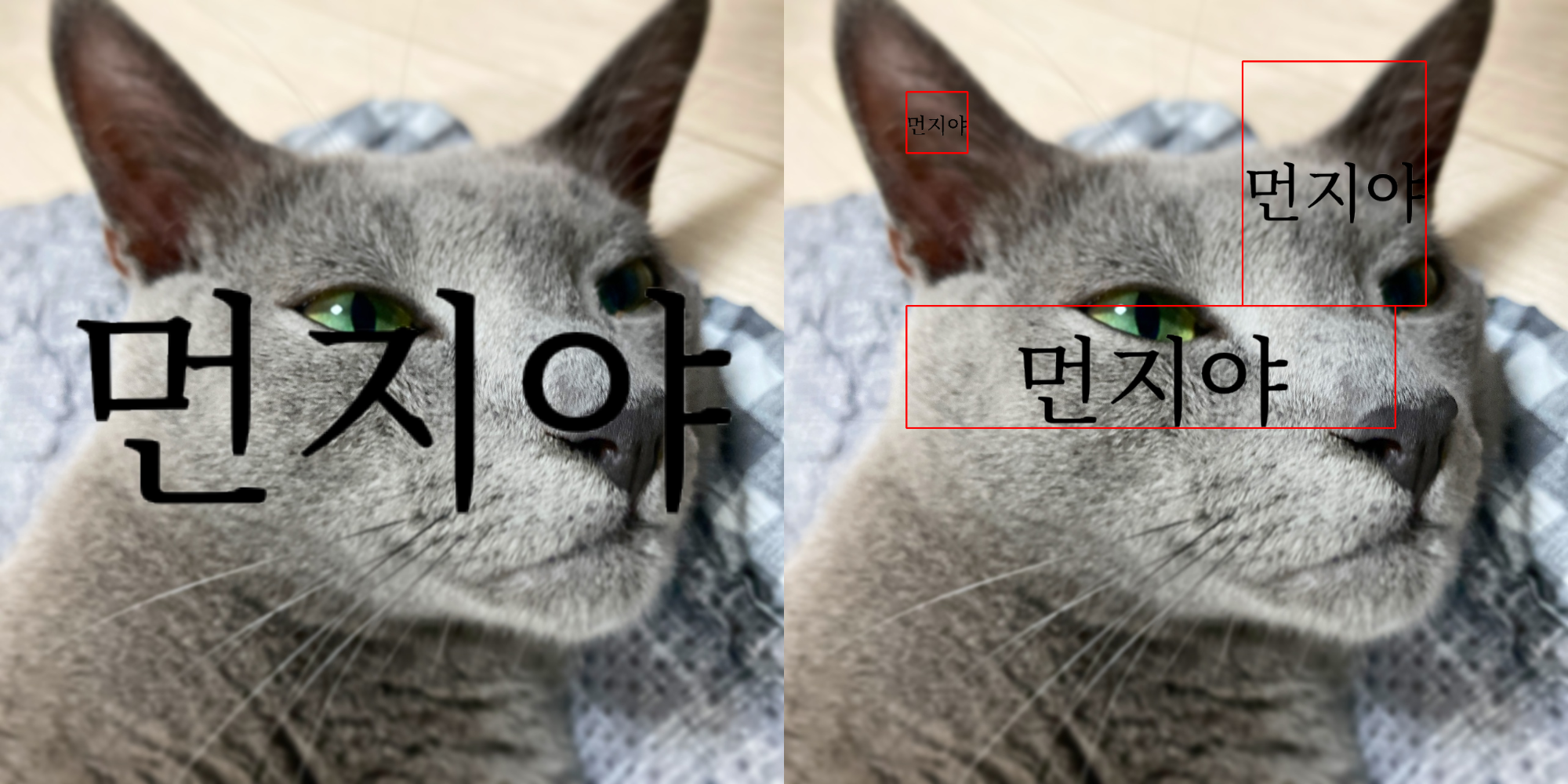
- zerohertzLib.vision.text(img, box, txt, color=(0, 0, 0), vis=False, fontsize=100)[source]¶
Text 시각화
- Parameters:
img¶ (
NDArray[np.uint8]) – 입력 image ([H, W, C])box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) – 문자열이 존재할 bbox ([4],[N, 4],[4, 2],[N, 4, 2])txt¶ (
Union[str, List[str]]) – Image에 추가할 문자열color¶ (
Optional[Tuple[int]]) – 문자의 색vis¶ (
Optional[bool]) – 문자 영역의 시각화 여부fontsize¶ (
Optional[int]) – 문자의 크기
- Returns:
시각화 결과 (
[H, W, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[np.uint8]
Examples
- Bbox:
>>> box = np.array([[100, 200], [100, 1000], [1200, 1000], [1200, 200]]) >>> box.shape (4, 2) >>> res1 = zz.vision.text(img, box, "먼지야")
- Bboxes:
>>> boxes = np.array([[250, 200, 100, 100], [600, 600, 800, 200], [900, 300, 300, 400]]) >>> boxes.shape (3, 4) >>> res2 = zz.vision.text(img, boxes, ["먼지야", "먼지야", "먼지야"], vis=True)
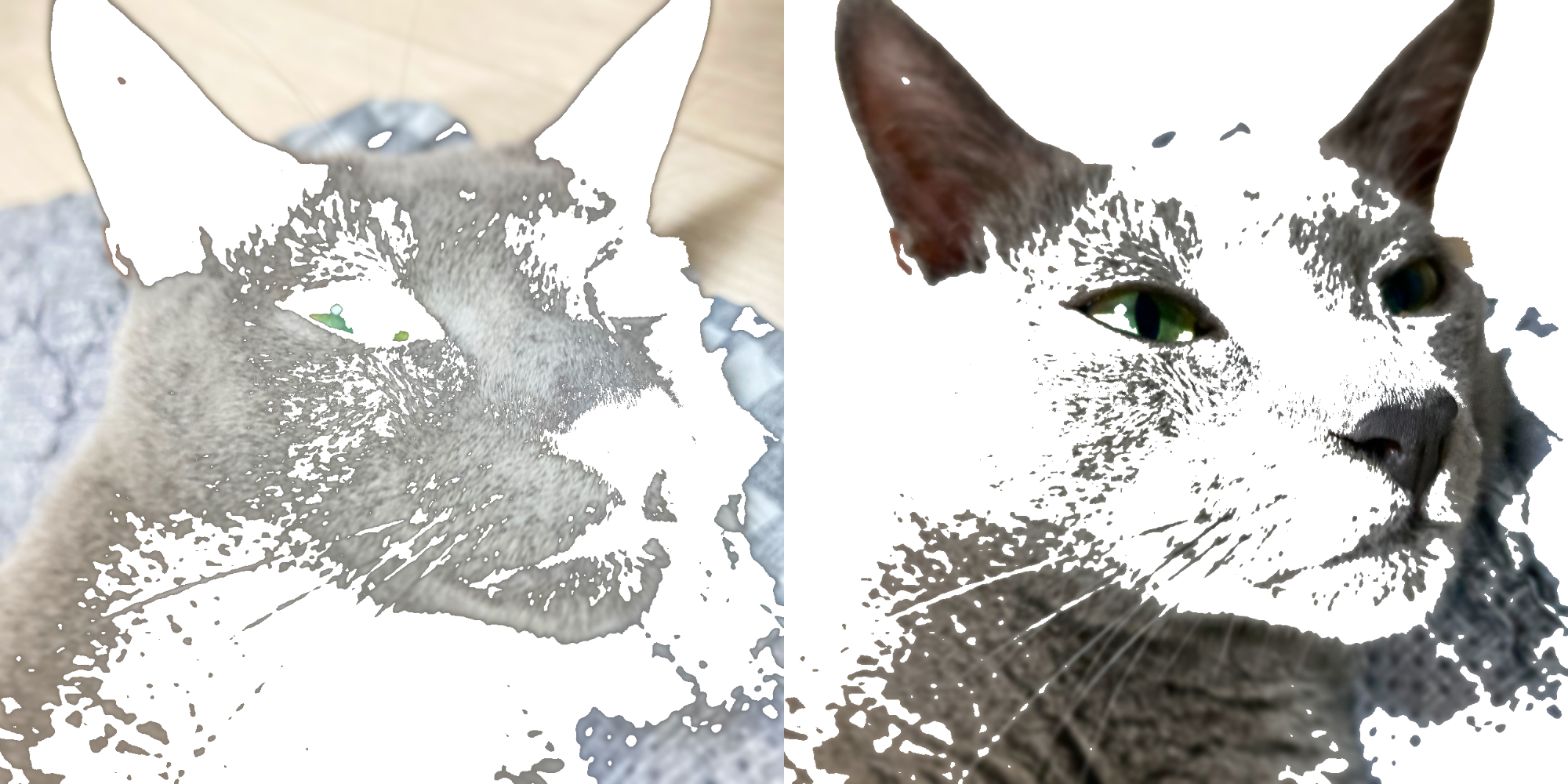
- zerohertzLib.vision.transparent(img, threshold=128, reverse=False)[source]¶
입력 image에 대해
threshold미만의 pixel들을 투명화- Parameters:
- Returns:
출력 image (
[H, W, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[np.uint8]
Examples
>>> res1 = zz.vision.transparent(img) >>> res2 = zz.vision.transparent(img, reverse=True)

- zerohertzLib.vision.vert(imgs, height=1000, file_name='tmp')[source]¶
여러 image를 입력받아 가로 image로 병합
- Parameters:
- Returns:
현재 directory에 바로 image 저장
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> imgs = [cv2.resize(img, (random.randrange(300, 600), random.randrange(300, 600))) for _ in range(5)] >>> zz.vision.vert(imgs)

- zerohertzLib.vision.vid2gif(path, file_name='tmp', quality=100, fps=15, speed=1.0)[source]¶
동영상을 GIF로 변환
- Parameters:
- Returns:
현재 directory에 바로 GIF 저장
- Return type:
None
Examples
>>> zz.vision.vid2gif("test.mp4")

- zerohertzLib.vision.xyxy2cwh(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[x0, y0, x1, y1]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Returns:
[cx, cy, w, h]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.xyxy2cwh([10, 20, 30, 40]) array([20, 30, 20, 20]) >>> zz.vision.xyxy2cwh(np.array([[10, 20, 30, 40], [30, 50, 70, 100]])) array([[20, 30, 20, 20], [50, 75, 40, 50]])
- zerohertzLib.vision.xyxy2poly(box)[source]¶
Bbox 변환
- Parameters:
box¶ (
Union[List[Union[int, float]], NDArray[DTypeLike]]) –[x0, y0, x1, y1]로 구성된 bbox ([4]or[N, 4])- Returns:
[[x0, y0], [x1, y1], [x2, y2], [x3, y3]]로 구성된 bbox ([4, 2]or[N, 4, 2])- Return type:
NDArray[DTypeLike]
Examples
>>> zz.vision.xyxy2poly([10, 20, 30, 40]) array([[10, 20], [30, 20], [30, 40], [10, 40]]) >>> zz.vision.xyxy2poly(np.array([[10, 20, 30, 40], [30, 50, 70, 100]])) array([[[ 10, 20], [ 30, 20], [ 30, 40], [ 10, 40]], [[ 30, 50], [ 70, 50], [ 70, 100], [ 30, 100]]])