Generative Adversarial Network (4)
DCGAN
- ANN generator의 문제점
- 부드러운 이미지가 아닌 고대비 픽셀로 이뤄진 불명확한 이미지
- 완전 연결 신경망은 메모리를 많이 사용하고 큰 이미지에 적합하지 않음
- 합성곱 GAN (Deep Convolutional Generative Adversarial Network, DCGAN)을 통해 극복
Localized Image Feature
- 이미지 데이터의 특성: 머신러닝을 위한 유의미한 특성 (feature)은 이미지에서 지역화된 (localized) 특성
- Ex) 눈과 코를 나타내는 픽셀은 서로 가까이 존재
- ANN generator
- 이러한 도메인 지식 (domain knowledge) 이용 불가
- 이미지의 모든 픽셀 항상 고려 (이미지 특성의 지역성 고려 X) $\rightarrow$ 비효율적 훈련
Convolution Neural Network
- 합성곱 (convolution): 합성곱 커널 (convolution kernel)을 통해 이미지의 정보를 새로운 격자에 요약하는 방법
- 실제 이미지 픽셀과 요약된 이미지 픽셀 사이의 유사성 모색
- 특성 맵 (feature map): 합성곱 커널 레이어가 모서리 혹은 점과 같은 디테일한 저수준 특성을 요약한 정보
- 특성 맵에 다시 합성곱 커널의 레이어를 추가하여 더 추상적인 특성들의 조합으로 구성된 고수준 특성 취득 가능
- 합성곱 신경망 (convolution neural network, CNN): 이웃한 픽셀들의 작은 패턴에서 비롯된 중수준의 특성으로부터 이미지 내용을 통해 분류에 용이
- 커널의 형태를 네트워크로 훈련 (네트워크가 저수준, 중수준, 고수준의 이미지 특성 훈련)
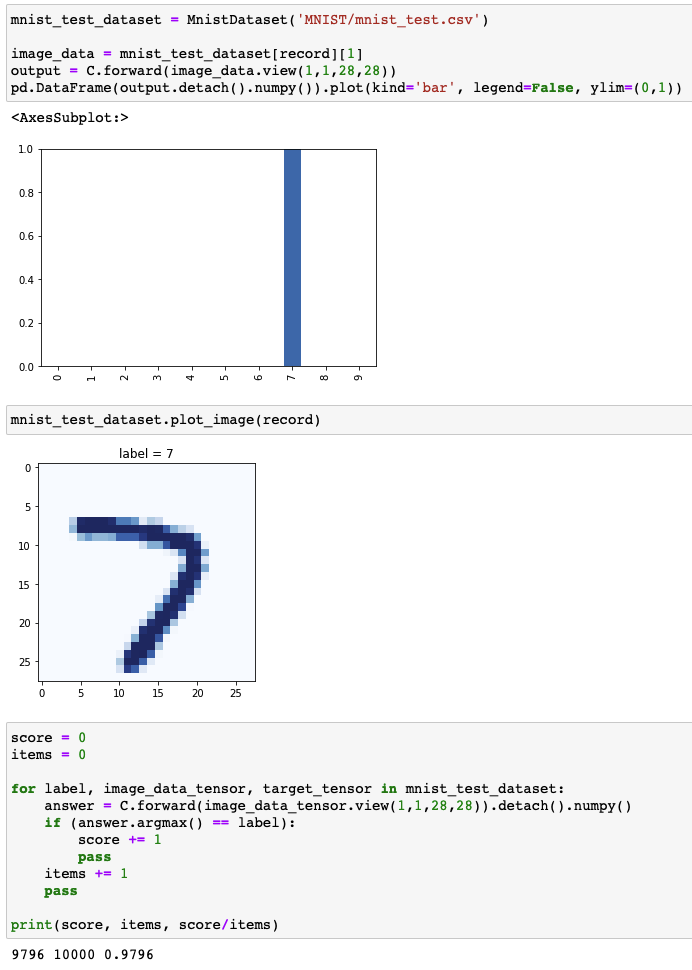
MNIST CNN
1 | ... |
1 | C = Classifier() |
nn.Conv2d(1, 10, kernel_size = 5, stride = 2): 합성곱 레이어- 입력 채널의 개수: 1 (단색 이미지)
- 출력 채널의 개수: 10
- 10개의 특성 맵으로 작동할 10개의 합성곱 커널 제작
kernel_size: 커널의 크기 설정stride(보폭): 이미지를 따라 커널이 얼마나 움직일지 설정- $5\times5$ 커널이 2칸씩 이동
nn.BatchNorm2d(10): 특성 맵 레이어의 전 채널 정규화nn.Conv2d(10, 10, kernel_size = 3, stride = 2)- 10개의 특성 맵에 $3\times3$ 커널을
stride = 2로 적용하여 $5\times5$인 10개의 특성맵 수집
- 10개의 특성 맵에 $3\times3$ 커널을
View(250)- $5\times5$ 크기의 특성 맵 10개 ($10\times5\times5=250$)를 받아 1차원 리스트에 할당
PyTorch의 합성곱 필터 요소:batch_size,channels,height,width(4차원 텐서)- MNIST 이미지는 단색이므로
channels = 1 (1, 1, 28, 28)
- MNIST 이미지는 단색이므로
Results of CNN applied to MNIST dataset
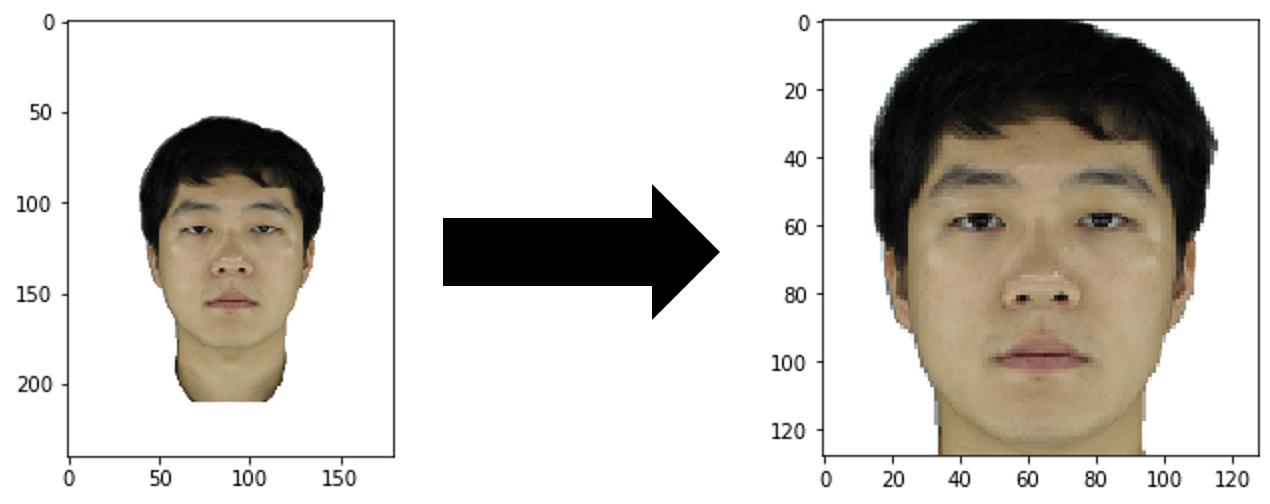
Montage DCGAN
1 | def crop_center(img, new_width, new_height): |
crop_center():numpy이미지 행렬을 받아 중앙에서부터 주어진 크기에 맞춰 절삭
1 | ... |
crop_center(img, 128, 128)
__getitem__()(height, width, 3)$\rightarrow$(batch_size, channels, height, width)permute(2, 0, 1):numpy행렬 순서 변환 ((height, width, 3)$\rightarrow$(3, height, width))View(1, 3, 128, 128): 배치 크기 1 추가
- Add
crop_center()
plot_image()- Add
crop_center()
- Add
1 | ... |
1 | ... |
- 판별기: 데이터가 레이어를 통과하며 데이터의 크기가 줄어들게 설계
- Raw image: $128\times128$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2\ \rightarrow$ 256 Feature map: $61\times61$
- 256 Feature map: $61\times61$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2\ \rightarrow$ 256 Feature map: $27\times27$
- 256 Feature map: $27\times27$ $\rightarrow$ 3 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2\ \rightarrow$ 3 Feature map: $10\times10$
- 생성기: 데이터가 레이어를 통과하며 데이터의 크기가 커지게 설계
- 전치 합성곱 (transposed convolution):
nn.ConvTranspose2d
- Seed: $100$ $\rightarrow$ $3\times11\times11$ $\rightarrow$ 4D Tensor: $(1,\ 3,\ 11,\ 11)$
- 4D Tensor: $(1,\ 3,\ 11,\ 11)$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Feature map: $28\times28$
- 256 Feature map: $28\times28$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2$ $\rightarrow$ 256 Feature map: $62\times62$
- 256 Feature map: $62\times62$ $\rightarrow$ 3 Kernel: $8\times8$ & Stride: $2$ & Padding: $1$ $\rightarrow$ 3 Feature map: $128\times128$ (generated image)
- 전치 합성곱 (transposed convolution):
- GELU (Gaussian Error Linear Unit): ReLU 함수와 비슷하지만 상대적으로 부드러운 곡선을 통해 개선된 기울기 제공
Results of DCGAN applied to montage dataset
CGAN
- 조건부 GAN (Conditional Generative Adversarial Network, CGAN): 클래스 레이블과 이미지 사이의 관계를 학습한 생산적 적대 신경망
- 훈련 시 시드에 입력을 추가하여 생성기가 주어진 클래스에 해당하는 이미지 생성
- 판별기 또한 클래스 레이블에 대한 정보 제공
Discriminator
1 | ... |
forward(): 이미지 텐서와 레이블 텐서를 동시 입력- 레이블 텐서: 원핫 인코딩 필수
Generator
1 | ... |
forward(): 이미지 텐서와 레이블 텐서를 동시 입력
Training and Results
1 | %%time |
- 실제 데이터에 대해 참으로 판별기 훈련:
D.train(image_data_tensor, label_tensor, torch.FloatTensor([1.0])) - 생성 데이터에 대해 거짓으로 판별기 훈련:
D.train(G.forward(generate_random_seed(100), random_label).detach(), random_label, torch.FloatTensor([0.0]))- 생성기에 임의의 시드와 임의의 레이블을 통해 이미지 생성
- 판별기에 생성된 이미지를 거짓으로 훈련
- 생성기 훈련:
G.train(D, generate_random_seed(100), random_label, torch.FloatTensor([1.0]))- 생성기에 임의의 시드와 임의의 레이블을 입력하여 이미지 생성
- 판별기에 생성된 이미지와 임의의 레이블을 함께 입력하여 판별기의 결과 출력
- 판별기의
loss_function에 출력된 결과와 실제 레이블을 입력하여loss값 출력
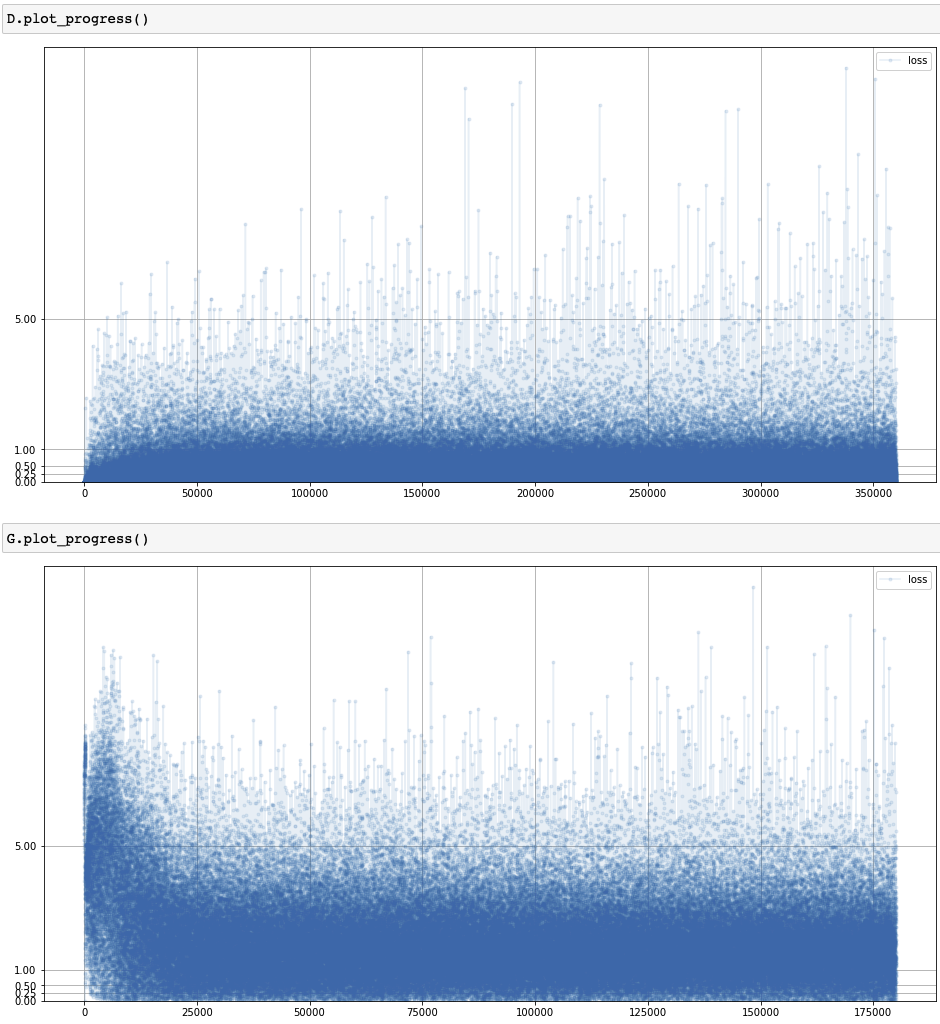
Loss of CGAN training process
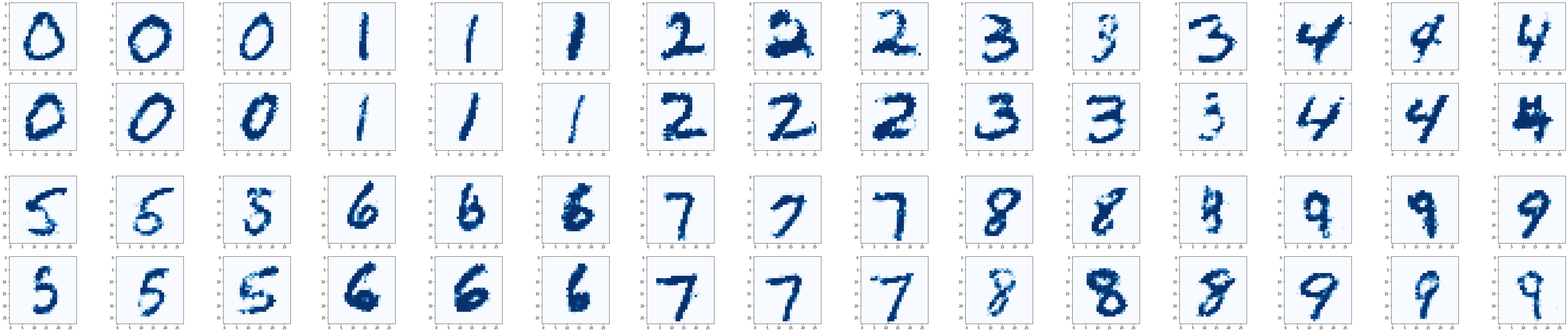
Results of CGAN applied to MNIST dataset: 0 ~ 9