Generative Adversarial Network (3)
MNIST Dataset
Data Description
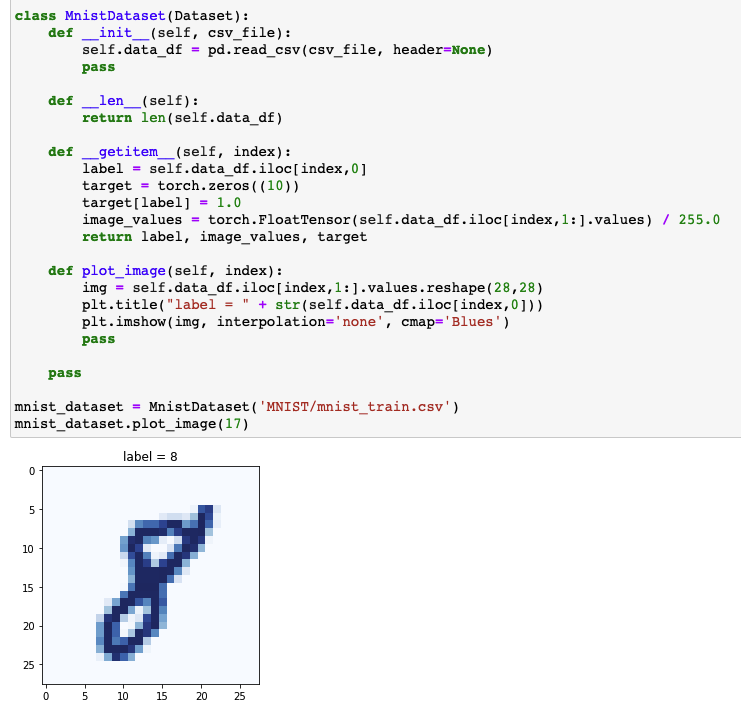
MNIST dataset
- Dataset 구성: 0 ~ 9의 손글씨 이미지 ($28\times28=784$)와 label
MnistDataset클래스Raw data$\rightarrow$TensorLabel,Pixel values,One-hot encoding tensor반환
- 목표: 생성기의 생성 이미지가 판별기를 속일 수 있도록 훈련
Discriminator
1 | class Discriminator(nn.Module): |
Discriminator training
- 실제 이미지 vs. 임의의 노이즈 분류 확인
Generator
1 | class Generator(nn.Module): |
- 생성기는 훈련 데이터의 여러 양상을 다양하게 반영해야 함
- 항상 정확히 같은 값 출력 X
- 0 ~ 9의 모든 이미지 생성
- 하지만 신경망의 같은 입력값에 대해서 항상 같은 출력
- 생성기의 입력으로 상수 X
- 매 훈련 사이클마다 임의 입력 필요 $\rightarrow$ Random Seed
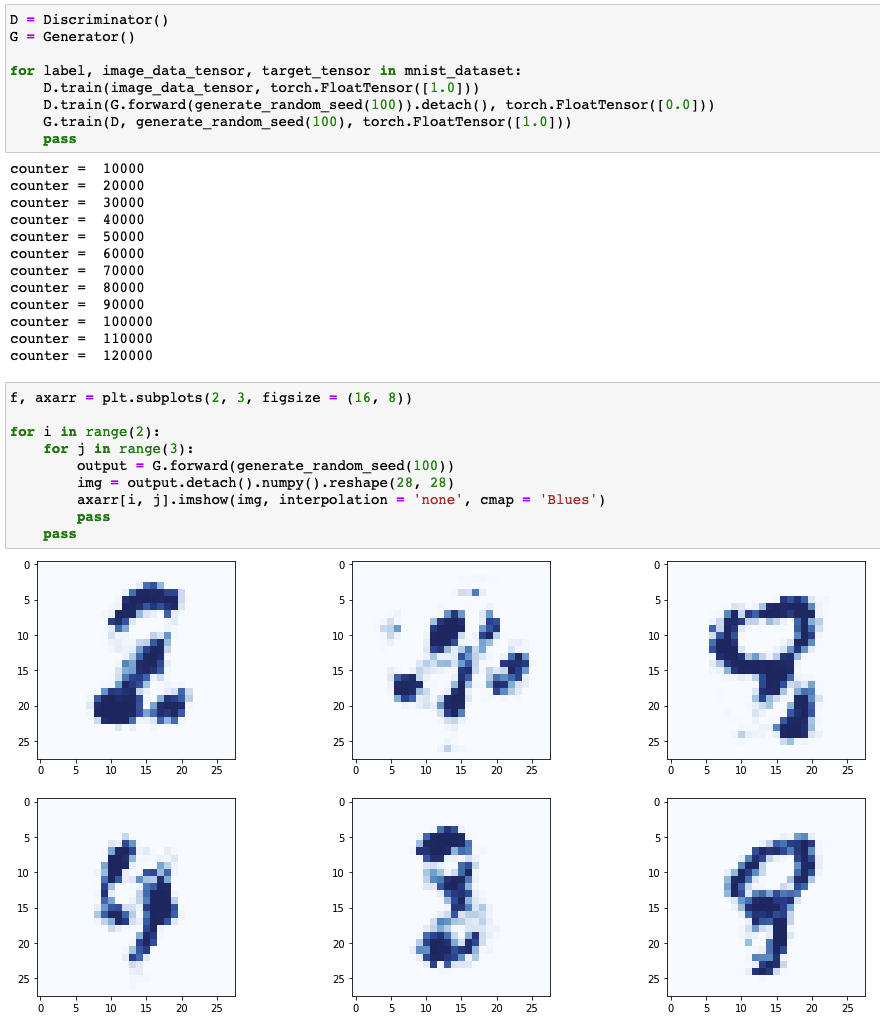
GAN Training
1 | %%time |
1 | %%time |
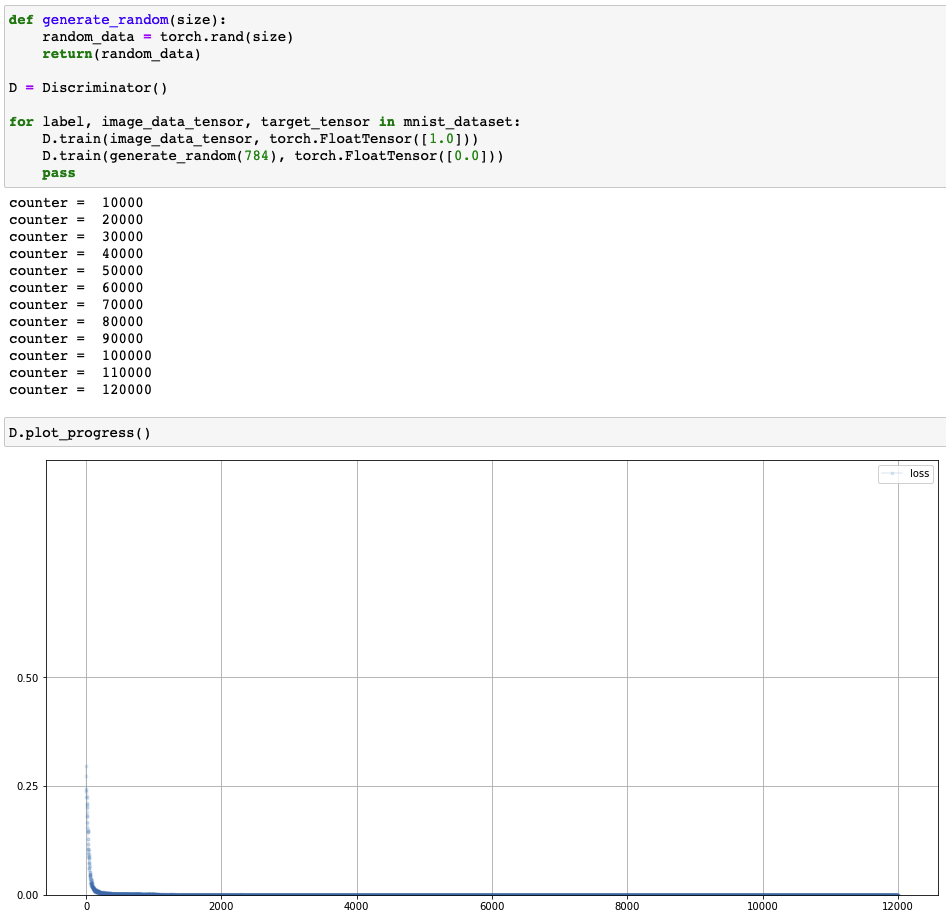
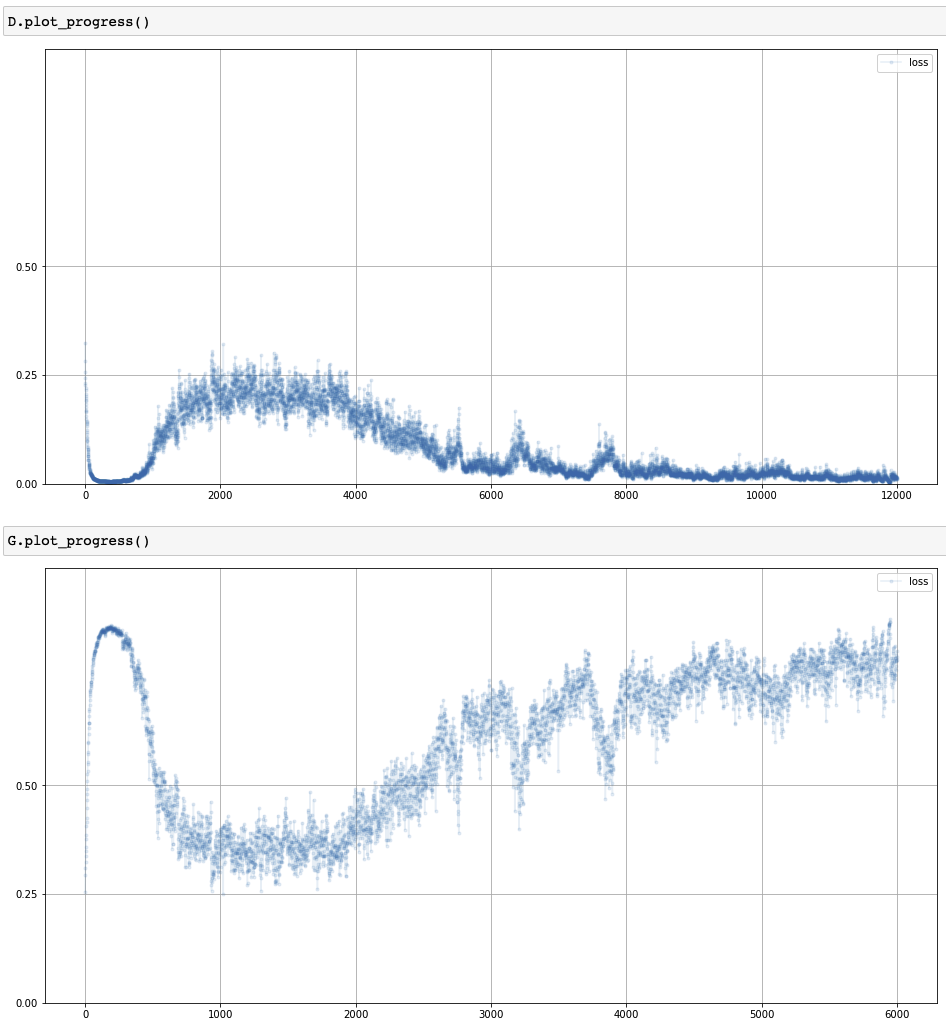
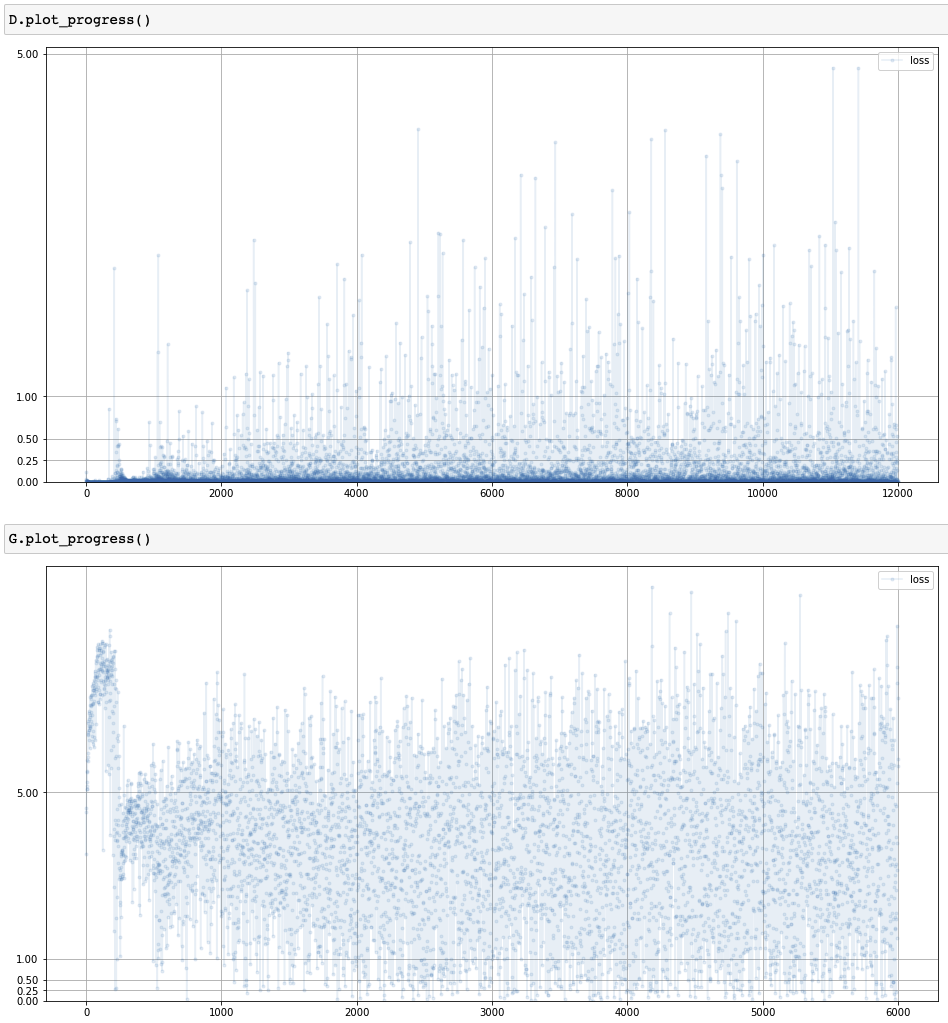
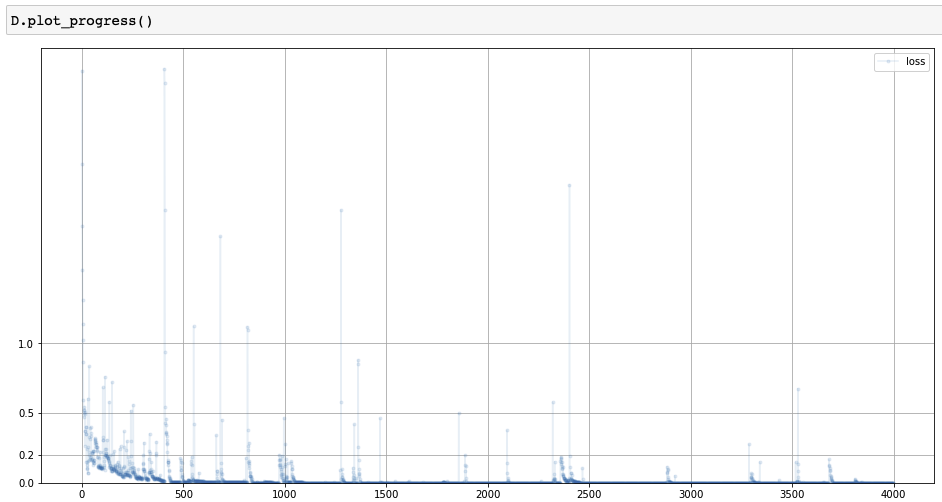
Loss of GAN training process
- Discriminator
- Loss: 0 $\rightarrow$ 0.25 $\rightarrow$ 0
- 판별기 > 생성기 $\rightarrow$ 판별기 = 생성기 $\rightarrow$ 판별기 > 생성기
- Generator
- Loss: 1 $\rightarrow$ 0.25 $\rightarrow$ 1
- 판별기 > 생성기 $\rightarrow$ 판별기 = 생성기 $\rightarrow$ 판별기 > 생성기
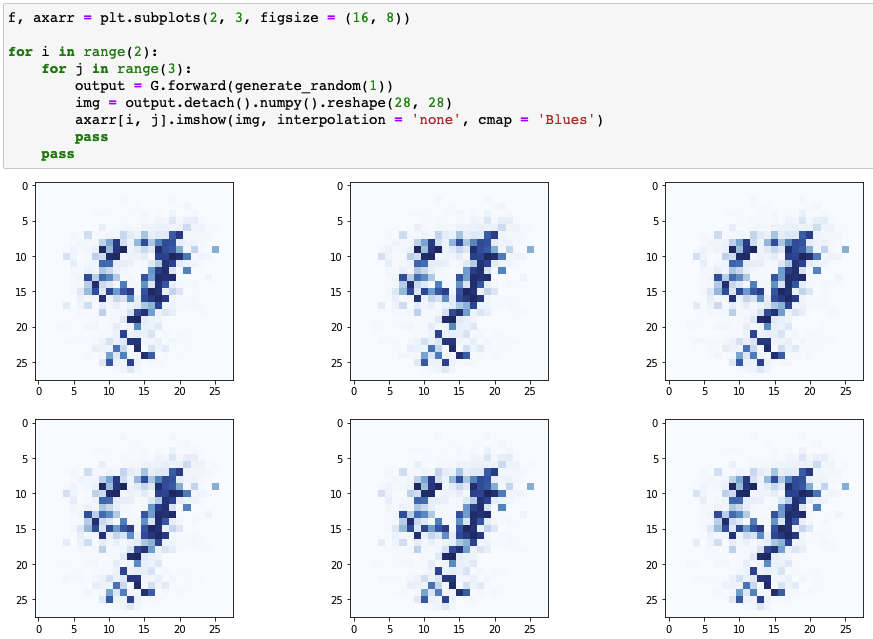
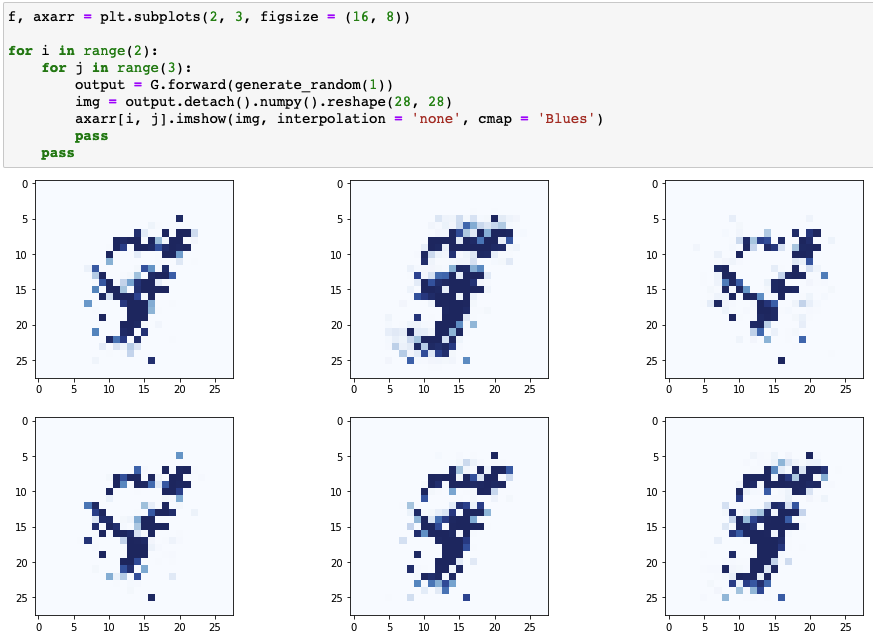
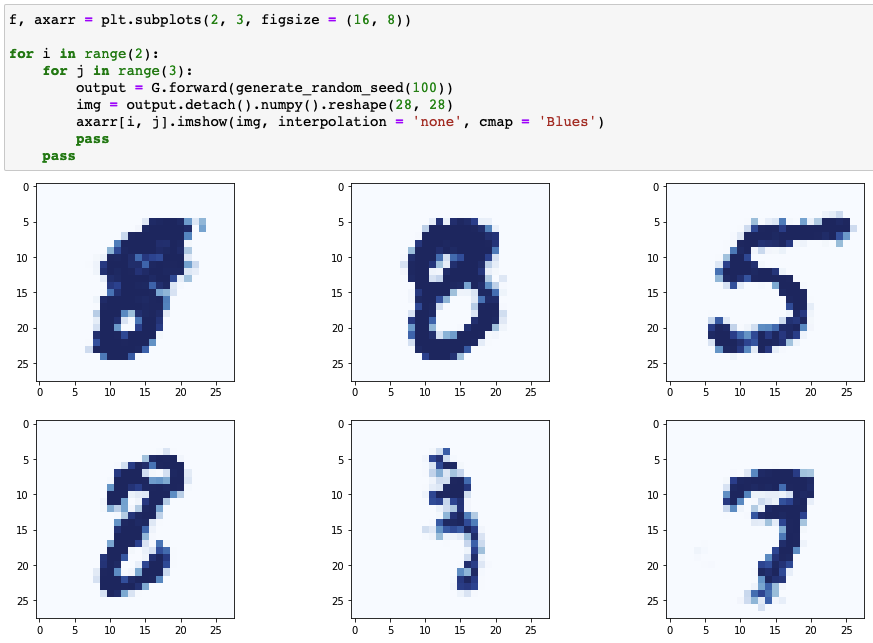
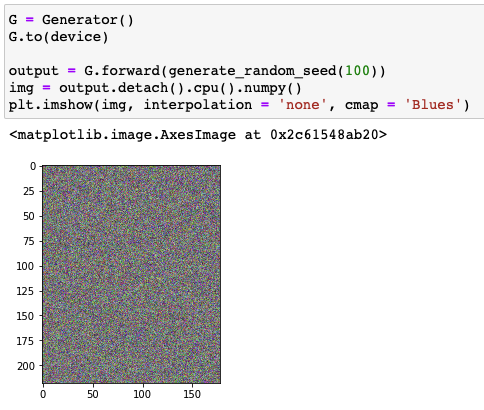
Results of generator
- 기존의 숫자 이미지들과 형상 유사
- 생성기 이미지들의 차이가 거의 없음
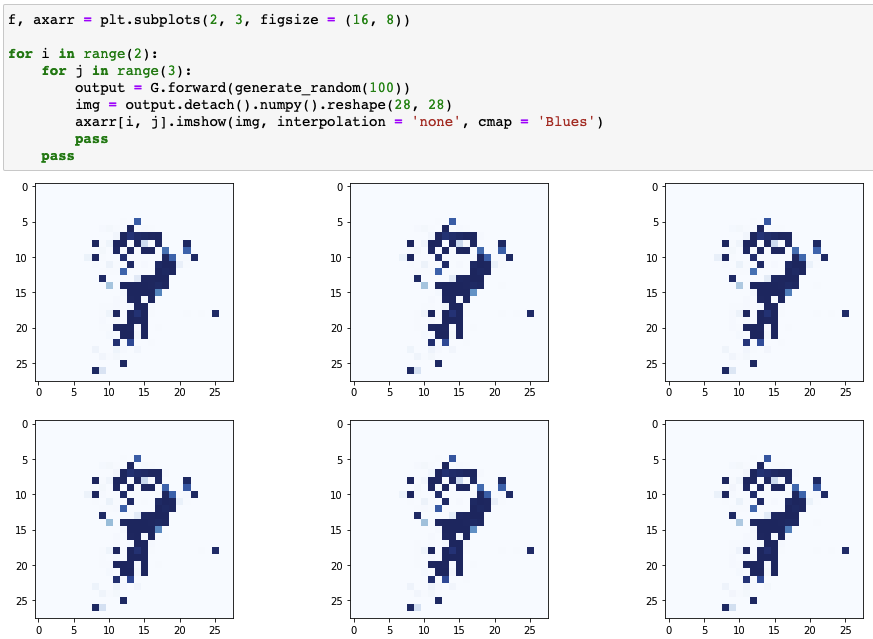
Mode Collapse
- Definition: 생성기가 다양한 label에 대한 이미지를 생성하지 못하고 하나 또는 극히 일부의 이미지만 생성
- 발생 이유는 명확히 규명되지 않음
- 생성기가 판별기보다 더 앞서간 후 항상 실제에 가깝게 결과가 나오는 지점에 대해서만 이미지를 만들어내는 가능성 존재
- 손실이 높아지는 구간에서는 학습이 진행되지 않음 (생성기의 성능 향상 불가)
- 훈련의 질 중요
1 | class Discriminator(nn.Module): |
Results of advanced generator: edit activation function, layer, optimizer
- 생성기의 이미지가 조금 더 선명해지고 서로 식별이 약간 가능해졌지만 숫자의 형태라고 보기엔 어려움
- 하나의 시드를 통해 10개 숫자에 대한 784개의 픽셀을 생성하는 것을 시도하기 때문에 개선 필요
1 | ... |
Results of advanced generator: edit random seed size
- 여전히 모드 붕괴 발생
- 판별기에 입력되는 임의의 이미지 픽셀 값은 0에서 1 사이에서 고르게 선택
- 0 ~ 1: 실제 데이터셋 기반 값
- 정규분포와 같은 경향성 없이 선택
- 생성기 투입 시드: 평균이 0이고 분산이 1인 분포에서 선택
- 신경망에서 평균이 0이고 분산이 제한된 정규화된 값들이 학습에 유리
1 | def generate_random_image(size): |
Results of advanced generator: edit random seed
- 모드 붕괴가 해결되어 다른 종류의 숫자 이미지를 생성기가 생성 가능
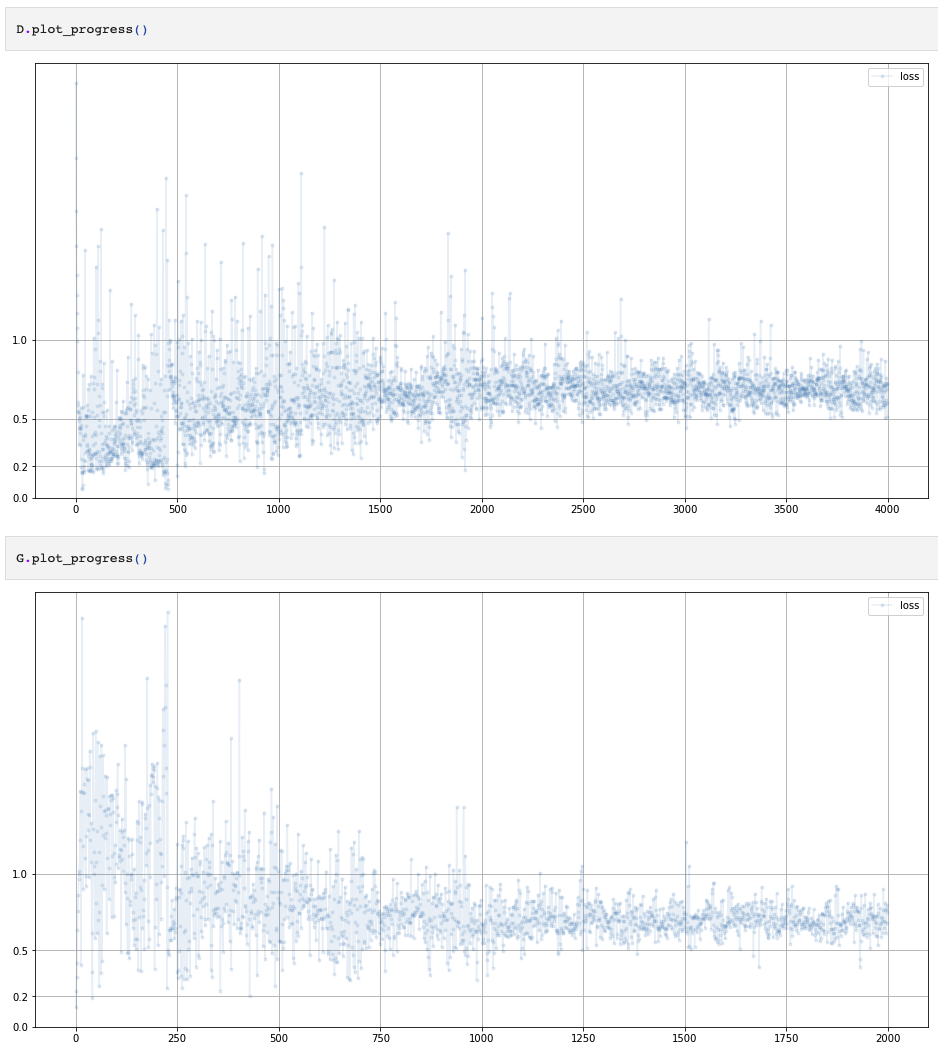
Loss of advanced GAN training process
BCELoss(): 이진 교차 엔트로피의 수학적 정의에 의해 $\ln(2)=0.693$이 이상적 손실- 모드 붕괴의 해결책이 무조건
randn()의 사용 혹은 시드의 수를 증가시키는 것은 아님- GAN에서 생성기와 판별기의 균형을 맞추는 것은 상당히 어려운 과정
- 균형이 맞지 않더라도 생성기의 성능이 나쁘지 않을 수 있음
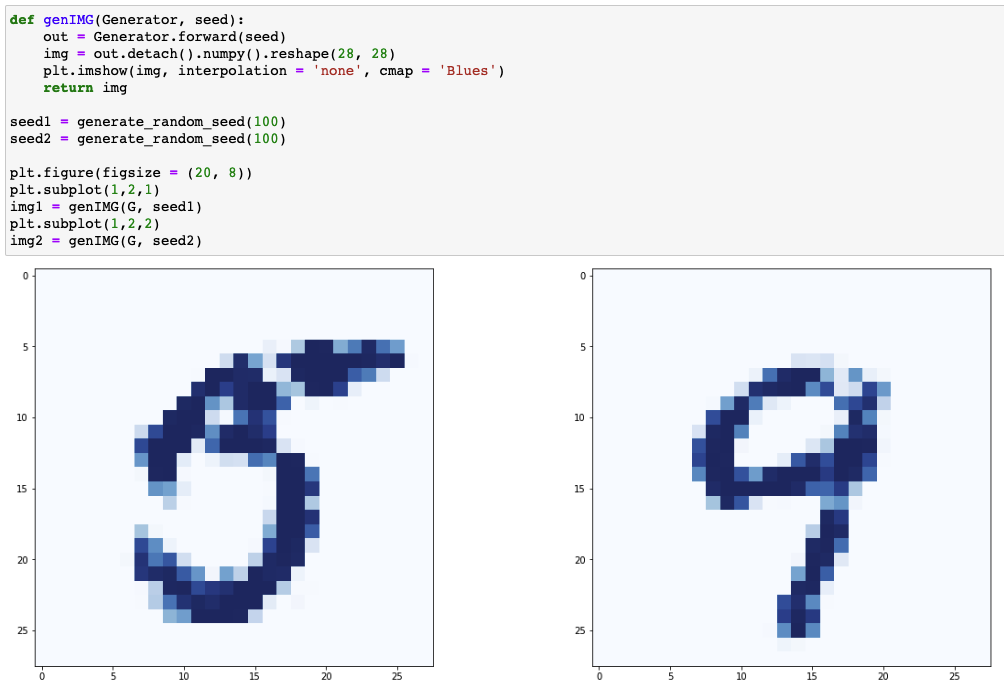
Random Seed
- 두가지 seed를 이용해 그 사이에 존재하는 seed들에 의해 생성기에 의해 생성된 이미지 실험
Results of advanced generator: edit epoch
Images generated by seed1 and seed2
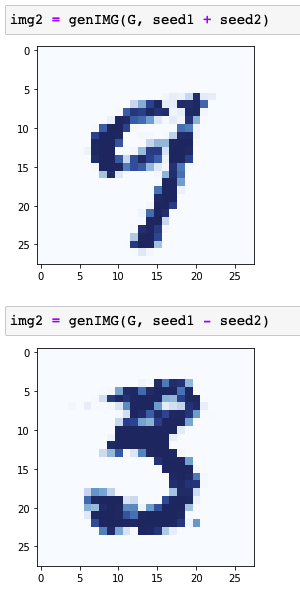
Images generated by seed1 + seed2 and seed1 - seed2
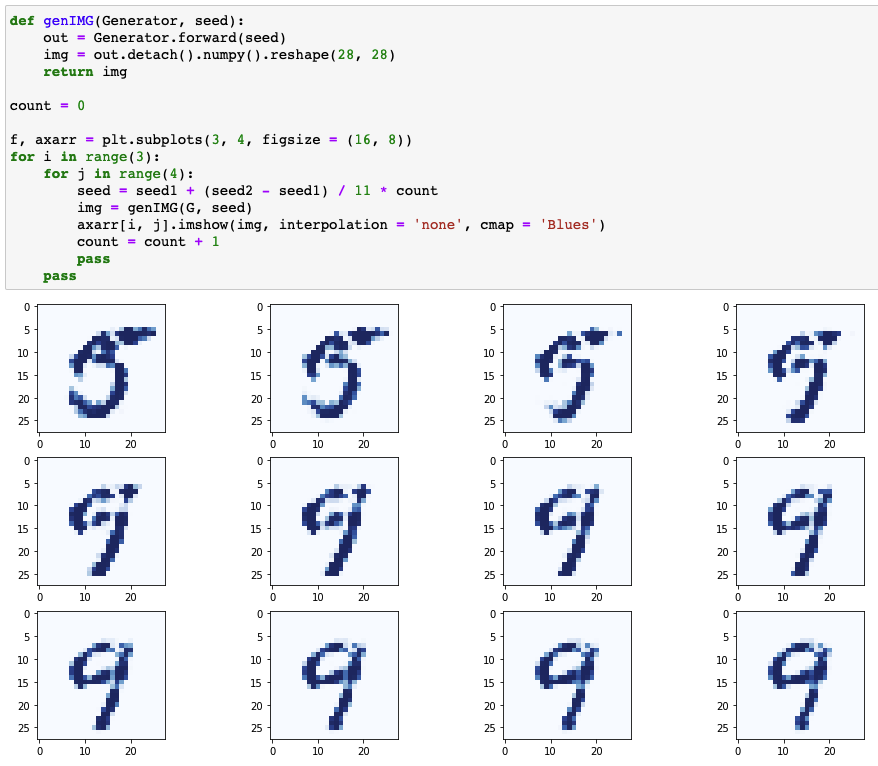
Images generated by seeds between seed1 and seed2
Face Image
- 3차원 (RGB) 풀컬러 이미지 훈련 및 생성
- $M\times N\times3$
- 사진의 훈련 데이터셋을 이용 및 다양하고 실제적 결과 산출
CelebA Dataset
- 202,599개의 유명인 얼굴 이미지
- 눈과 입의 위치가 비슷한 좌표에 위치하도록 조정됨 (aligned)
CelebA Dataset
Hierarchical Data Format
- 다수의
.jpeg파일 $\rightarrow$ 훈련 과정에서 열고 닫을 시 시간 소모 큼 $\rightarrow$ HDF5 사용 - HDF (Hierarchical Data Format, 계층적 데이터 형식): 용량이 매우 큰 데이터에 효과적으로 접근하기 위해 만들어진 데이터 형식
- 하나 이상의 그룹을 가질 수 있어 계층적이라 불림
- 그룹 안에 여러 개의 데이터셋이 포함될 수 있음
- HDF5 (HDF version 5)를 이용해 훈련 과정에서의 시간 소모 개선 및 메모리의 한계 극복
1 | import torchvision.datasets |
import h5py: HDF5 파일을 다루기 위한 라이브러리- $218\times178\times3$: 높이 218픽셀, 너비 178픽셀, RGB
1 | class CelebADataset(Dataset): |
__init__(): HDF5 파일을 열고img_align_celeba로 각각의 이미지에 접근__len__(): 그룹 안의 데이터 수 반환__getitem__(): Index를 이미지의 이름으로 변환하고 이미지 데이터 반환
Discriminator
1 | class View(nn.Module): |
- 이미지가 실제인지 생성된 이미지인지 분류
- 입력: $218\times178\times3=116412$
- 신경망이 완전 연결 신경망이므로 일관된 기준을 통해 정렬
- 이미지를 어떻게 풀어서 정렬하는지는 중요하지 않음
View(): 3차원 이미지 텐서를 1차원 형태의 텐서로 변환- $(218,178,3)\rightarrow(218\times178\times3)$
nn.Module을 상속하여Sequential내에서 다른 모듈과 함께 사용 가능
1 | %%time |
Discriminator test
Generator
1 | class Generator(nn.Module): |
- 3차원의 텐서를 $(218,178,3)$의 크기로 결과를 출력하도록 수정
- $100\rightarrow300\rightarrow3\times218\times178\rightarrow(218,178,3)$
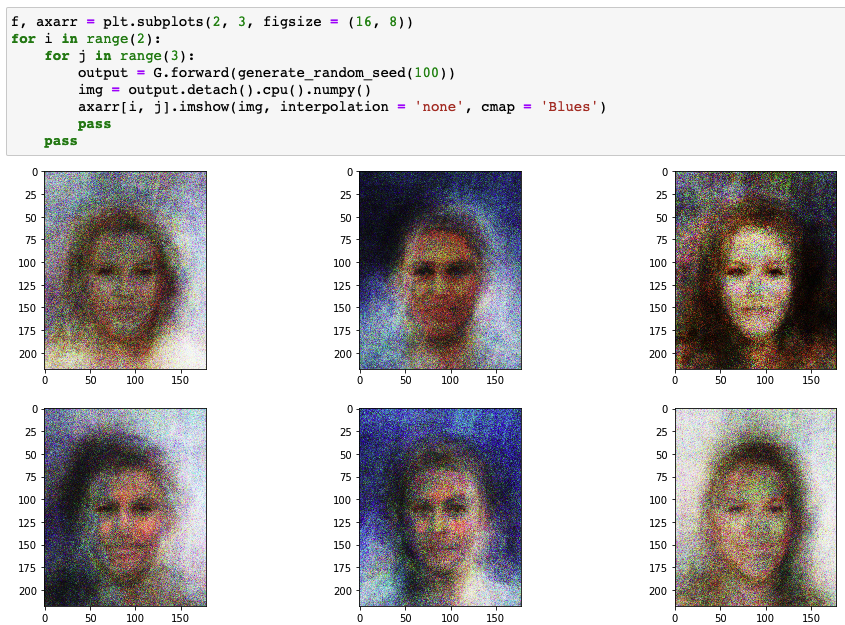
Result of generator
GAN Training
1 | %%time |
Loss of GAN training process
Results of generator
- 생성기는 직접 이미지를 통해 훈련하지 않고 이미지를 생성할 때 훈련 데이터의 우도 (likelihood) 사용