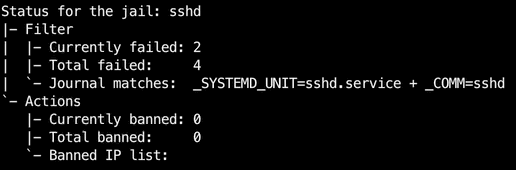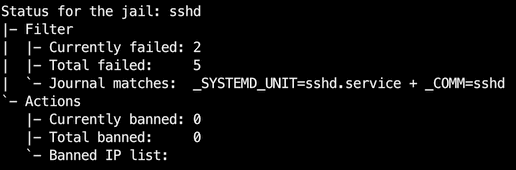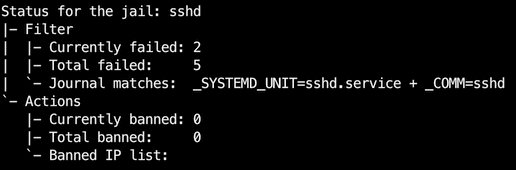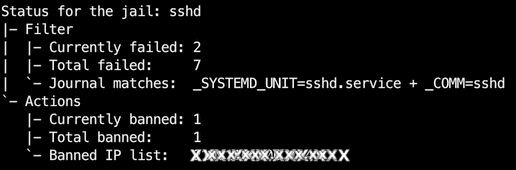
Introduction Fail2Ban 의 명령어 중 sudo fail2ban-client status sshd을 사용하면 아래와 같은 결과가 나온다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 $ sudo fail2ban-client status sshdStatus for the jail: sshd # Service에 대한 보호 규칙 |- Filter # 악의적인 활동 정보 | |- Currently failed: 2 # 2개 기기의 잘못된 로그인 시도 | |- Total failed: 7 # 시작된 이후 총 7번의 잘못된 로그인 시도 | `- Journal matches: _SYSTEMD_UNIT=sshd.service + _COMM=sshd # Fail2Ban의 시스템 로그를 감시 방법 `- Actions # 악의적인 활동을 감지했을 때 취하는 조치에 대한 정보 |- Currently banned: 1 # 현재 차단된 IP 주소의 수 |- Total banned: 1 # 총 차단된 IP 주소의 수 `- Banned IP list: XXX.XXX.XXX.XXX # 차단된 IP
차단된 기기에서 SSH를 연결하려 시도하면 아래와 같이 실패하게 된다.
1 2 $ ssh ${USER} @${IP} -p ${PORT} ssh: connect to host ${IP} port ${PORT}: Connection refused
이걸 매번 확인할 수는 없기 때문에 의문의 중국 해커가 공격하면 알람을 받을 수 있게 Apache Airflow와 Discord를 사용해보겠다!사실 그거 안다해도 포맷 말고 할 수 있는게 없긴 한…
Setup Test 환경을 구축하기 위해 Conda를 설치한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 $ wget https://repo.anaconda.com/archive/Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh $ bash Anaconda3-2021.05-Linux-x86_64.sh $ source /home/${USER} /anaconda3/bin/activate$ conda init $ source ~/.bashrc$ conda env list # conda environments: # base * /home/${USER} /anaconda3 $ conda create -n test python=3.8 -y $ conda activate test
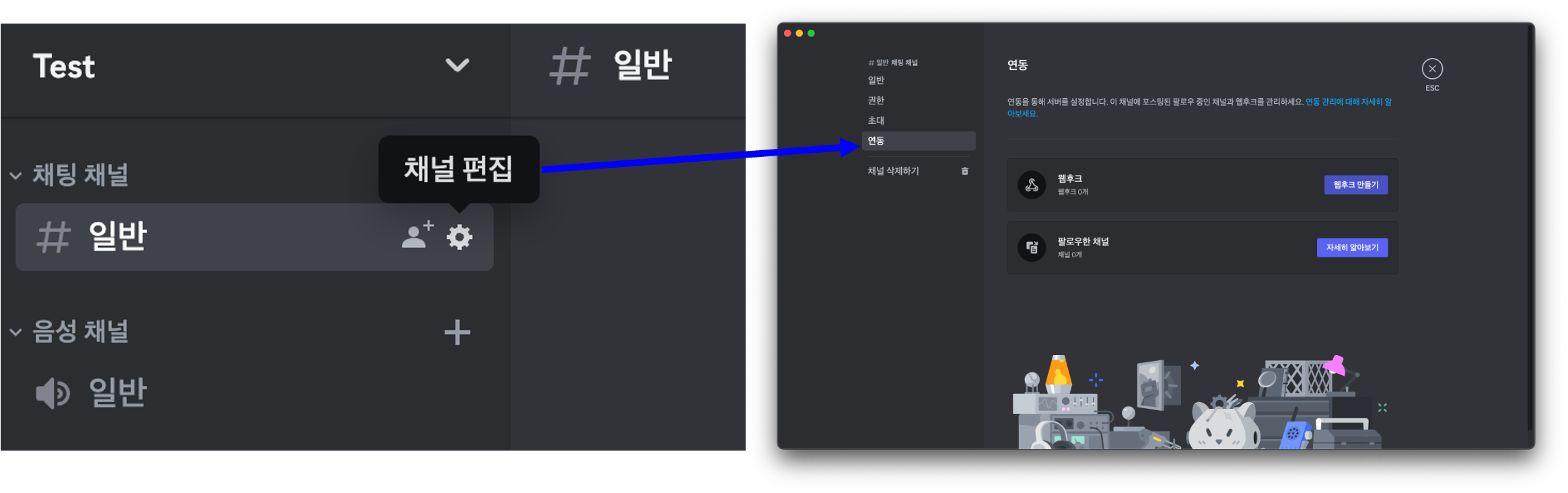
Discord에서 Webhook과 Bot의 차이는 아래와 같다.
항목
Webhook
Bot
목적
특정 이벤트에 따른 자동 메시지 전송
사용자와의 상호작용 및 다양한 작업 수행
상호작용
없음
사용자와 상호작용 가능
인증
웹훅 URL을 통한 인증
토큰을 사용한 인증
설정 및 관리
Discord 서버의 특정 채널에서 설정 및 관리
Discord Developer Portal에서 생성 및 관리
진행하려는 service의 목표는 event 발생 시 Discord로 단순 메시지를 전송하는 것이므로 Webhook를 사용한다.
웹후크 URL 복사 버튼을 누르면 끝이다!
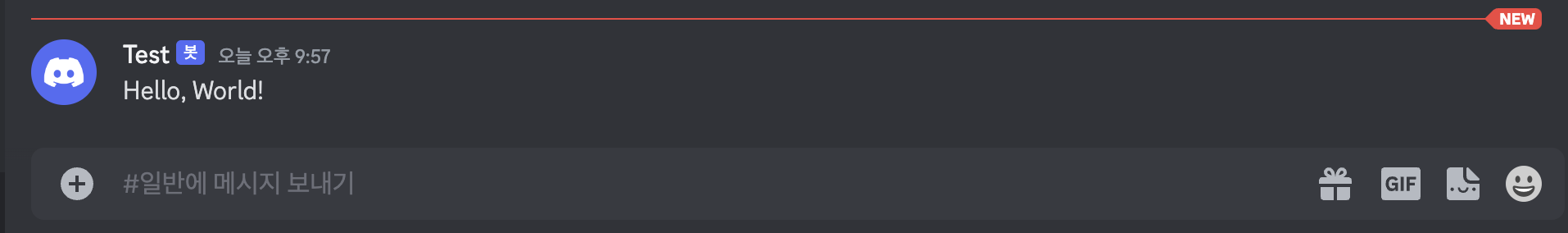
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 import requestsimport jsondef send_discord_message (webhook_url, content ): data = { "content" : content } headers = { "Content-Type" : "application/json" } response = requests.post(webhook_url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers) return response >>> webhook_url = "${WEBHOOK_URL}" >>> message = "Hello, World!" >>> response<Response [204 ]>
아주 잘 수신이 되는 것을 확인했다.
DAG
BashOperator
sudo fail2ban-client status sshd 실행결과를 다음 task에 전달
PythonOperator
이전 단계의 결과와 적재된 결과 비교
다르다면 log 파일을 작성하고 Webhook으로 메시지 전달
하지만 sudo fail2ban-client status sshd 명령어는 pod 바깥의 사용자 계정에서 실행되어야 한다.BashOperator를 사용하는 것이 의미가 없다.KubernetesPodOperator을 사용해서 /var/log/fail2ban.log가 /opt/airflow/logs/fail2ban.log에 마운트 되도록 구성해보자!
KubernetesPodOperator그 전에 KubernetesPodOperator를 알아보고 예제를 살펴보자. (PythonOperater 등이 실행되는 pod의 기본 설정은 여기 를 참고)
Docker Image
지정된 Docker image를 사용하여 작업 실행
커스텀 로직이나 의존성을 가진 코드를 실행할 때 유용
Dynamic Environment
Kubernetes를 사용하여 작업별로 독립된 환경 제공
각 작업의 독립적인 환경 실행 보장
서로 다른 작업들 사이에서 의존성 충돌 회피 가능
Parameterization
다양한 파라미터를 통해 pod의 설정 제어
Pod의 resource 제한, environment variables, volume mounts, …
XCom Integration
XCom을 통해 데이터를 Airflow의 다른 작업과 공유
/airflow/xcom/return.json 경로에 데이터를 작성함으로써 XCom 값을 반환
Logging
get_logs 파라미터를 사용하여 pod에서 생성된 로그를 Airflow UI에 출력
Resource Management
Pod의 생성과 제거, 그리고 에러 핸들링 등의 lifecycle을 Airflow에서 관리
test.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 import jsonimport airflowimport requestsfrom airflow.decorators import dagfrom airflow.operators.python import PythonOperatorfrom airflow.providers.cncf.kubernetes.operators.kubernetes_pod import ( KubernetesPodOperator, ) def _print_contexts (**kwargs ): print ("=" * 100 ) ti = kwargs["ti" ] result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator = ti.xcom_pull( task_ids="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" ) print ("result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator:\t" , result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator) print ("=" * 100 ) @dag( dag_id="test" , start_date=airflow.utils.dates.days_ago(0 schedule_interval="@hourly" , max_active_runs=1 , catchup=False , def test (): test_kubernetes_pod_operator = KubernetesPodOperator( task_id="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , name="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , image="ubuntu" , cmds=["/bin/bash" , "-c" ], arguments=[ """mkdir -p /airflow/xcom/;echo '{"Log": "Hello, World!"}' > /airflow/xcom/return.json""" ], labels={"foo" : "bar" }, do_xcom_push=True , ) print_contexts = PythonOperator( task_id="print_contexts" , python_callable=_print_contexts, ) test_kubernetes_pod_operator >> print_contexts DAG = test()
예제는 KubernetesPodOperator인 test_kubernetes_pod_operator가 {"Log": "Hello, World!"}를 XCom에 작성하고 PythonOperator인 print_contexts을 통해 아래와 같이 출력한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 ... {pod.py:524} INFO - xcom result: {"Log" : "Hello, World!" } ... ... {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ==================================================================================================== {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator: {'Log' : 'Hello, World!' } {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ==================================================================================================== ...
전략을 바꿔서 아래와 같이 구성해보겠다.
KubernetesPodOperator
/var/log/fail2ban.log 마운트fail2ban.log를 다음 task에 전달 (/airflow/xcom/return.json)
PythonOperator
이전 단계의 결과와 적재된 결과 비교
다르다면 log 파일을 작성하고 Webhook으로 메시지 전달
먼저 fail2ban.log를 읽고 /airflow/xcom/return.json를 작성하는 Python 코드를 개발하기 전 테스트를 해보자.
get_files.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import jsonimport osif __name__ == "__main__" : res = {} res["Abs" ] = os.getcwd() res["Results" ] = os.listdir() os.makedirs("/airflow/xcom" , exist_ok=True ) print (res) with open ("/airflow/xcom/return.json" , "w" ) as f: json.dump(res, f)
Dockerfile 1 2 3 4 5 6 FROM python:3.8 WORKDIR /app COPY get_files.py . CMD ["python" , "get_files.py" ]
1 $ docker build -t airflow-get-files:dev .
이렇게 생성된 이미지를 아래와 같은 DAG로 실행할 수 있다.
test2.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 import jsonimport airflowimport requestsfrom airflow.decorators import dagfrom airflow.operators.python import PythonOperatorfrom airflow.providers.cncf.kubernetes.operators.kubernetes_pod import ( KubernetesPodOperator, ) def _print_contexts (**kwargs ): print ("=" * 100 ) ti = kwargs["ti" ] result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator = ti.xcom_pull( task_ids="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" ) print ("result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator:\t" , result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator) print ("=" * 100 ) @dag( dag_id="test2" , start_date=airflow.utils.dates.days_ago(0 schedule_interval="@hourly" , max_active_runs=1 , catchup=False , def test2 (): test_kubernetes_pod_operator = KubernetesPodOperator( task_id="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , name="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , image="airflow-get-files:dev" , do_xcom_push=True , ) print_contexts = PythonOperator( task_id="print_contexts" , python_callable=_print_contexts, ) test_kubernetes_pod_operator >> print_contexts DAG = test2()
1 2 3 {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ==================================================================================================== {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator: {'Abs' : '/app' , 'Results' : ['get_files.py' ]} {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ====================================================================================================
잘 실행되는 것을 확인할 수 있다!PV, PVC를 K8s에 구성하고 KubernetesPodOperator에 연결해보자.
storage.yaml 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolume metadata: name: zerohertz-airflow-log-pv labels: type: zerohertz-airflow-log spec: storageClassName: airflow-storage capacity: storage: 10Gi accessModes: - ReadOnlyMany hostPath: path: "/var/log/fail2ban.log" --- apiVersion: v1 kind: PersistentVolumeClaim metadata: name: zerohertz-airflow-log-pvc namespace: airflow spec: storageClassName: airflow-storage accessModes: - ReadOnlyMany resources: requests: storage: 10Gi selector: matchLabels: type: zerohertz-airflow-log
kubectl apply -f storage.yaml로 K8s에 PV와 PVC를 생성하고 확인을 위해 Docker image에서 실행될 아래와 같은 Python 코드를 준비했다.
get_files.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 import jsonimport osdef print_tree (directory, prefix="" ): if os.path.isdir(directory): print (prefix + "├── " + os.path.basename(directory) + "/" ) prefix = prefix + "│ " for item in sorted (os.listdir(directory)): path = os.path.join(directory, item) if os.path.isdir(path): print_tree(path, prefix) else : print (prefix + "├── " + item) else : print (prefix + "├── " + os.path.basename(directory)) if __name__ == "__main__" : res = {} res["Abs" ] = os.getcwd() res["Results" ] = os.listdir() os.makedirs("/airflow/xcom" , exist_ok=True ) print (res) print_tree("/app" ) with open ("/airflow/xcom/return.json" , "w" ) as f: json.dump(res, f)
그리고 준비된 PV와 PVC를 DAG의 KubernetesPodOperator가 마운트하는 방법은 아래와 같다.
test3.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ... from kubernetes.client.models import V1Volume, V1VolumeMountvolume_mount = V1VolumeMount( name="zerohertz-airflow-log-volume" , mount_path="/app/fail2ban.log" , read_only=True ) volume_config = V1Volume( name="zerohertz-airflow-log-volume" , persistent_volume_claim={"claimName" : "zerohertz-airflow-log-pvc" }, ) ... def test3 (): test_kubernetes_pod_operator = KubernetesPodOperator( task_id="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , name="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" , image="airflow-get-files:dev" , do_xcom_push=True , volumes=[volume_config], volume_mounts=[volume_mount], ) ...
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 ... {pod_manager.py:367} INFO - {'Abs' : '/app' , 'Results' : ['fail2ban.log' , 'get_files.py' ]} {pod_manager.py:367} INFO - ├── app/ {pod_manager.py:367} INFO - │ ├── fail2ban.log {pod_manager.py:367} INFO - │ ├── get_files.py ... ... {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ==================================================================================================== {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator: {'Abs' : '/app' , 'Results' : ['fail2ban.log' , 'get_files.py' ]} {logging_mixin.py:149} INFO - ==================================================================================================== ...
XCom을 통한 Log 전송 마운트 된 fail2ban.log를 읽고, PythonOperator에 전달하기 위해 get_log.py를 개발하고 Docker image를 생성한다.
get_log.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 import jsonimport osif __name__ == "__main__" : res = {} with open ("fail2ban.log" , "r" ) as f: log = f.readlines() res["log" ] = log os.makedirs("/airflow/xcom" , exist_ok=True ) with open ("/airflow/xcom/return.json" , "w" ) as f: json.dump(res, f)
test4.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 ... def _print_contexts (ti ): result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator = ti.xcom_pull( task_ids="test_kubernetes_pod_operator" ) print ("result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator:\t" , result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator) ... >>> {logging_mixin.py:149 } INFO - result_from_kubernetes_pod_operator: {'log' : ['2023-08-13 04:24:32,227 fail2ban.server [127633]: INFO ---------- ...
출력이 잘 되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
Log 변경 감지 현재 로그 (current_log)와 적재된 로그 (past_log)의 길이를 비교하여 현재가 더 크다면 현재 로그를 적재하고 Discord Webhook에 두 로그의 길이 차이만큼 로그를 전달한다.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 ... def _check_jail (ti ): ... current_log = ti.xcom_pull(task_ids="get_current_log" ) current_log = current_log["log" ] try : with open (PAST_LOG_PATH, "r" ) as f: past_log = f.readlines() except : past_log = [] length_past_log, length_current_log = len (past_log), len (current_log) if length_past_log < length_current_log: with open (PAST_LOG_PATH, "w" ) as f: f.writelines(current_log) response = _send_discord_message(DISCORD_WEBHOOK, current_log[length_past_log:]) elif length_past_log > length_current_log: response = _send_discord_message( DISCORD_WEBHOOK, "ERROR: THE PAST LOG IS LONGER THAN CURRENT LOG" ) ...
최종 코드! 하지만 수많은 로그를 한번에 전송하거나 아주 긴 로그를 한번에 보낼 수 없다.
1 2 3 4 >>> _send_discord_message(DISCORD_WEBHOOK, "=" *2000 )<Response [204 ]> >>> _send_discord_message(DISCORD_WEBHOOK, "=" *2001 )<Response [400 ]>
따라서 아래와 같이 1초 및 줄 간격으로 메시지를 보내는 것으로 구현했다.
Jail.py 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 import jsonimport timeimport airflowimport requestsfrom airflow.decorators import dagfrom airflow.operators.python import PythonOperatorfrom airflow.providers.cncf.kubernetes.operators.kubernetes_pod import ( KubernetesPodOperator, ) from kubernetes.client.models import V1Volume, V1VolumeMountvolume_mount = V1VolumeMount( name="zerohertz-airflow-log-volume" , mount_path="/app/fail2ban.log" , read_only=True ) volume_config = V1Volume( name="zerohertz-airflow-log-volume" , persistent_volume_claim={"claimName" : "zerohertz-airflow-log-pvc" }, ) def _send_discord_message (webhook_url, content ): data = {"content" : content} headers = {"Content-Type" : "application/json" } response = requests.post(webhook_url, data=json.dumps(data), headers=headers) return response def _check_jail (ti ): DISCORD_WEBHOOK = "${DISCORD_WEBHOOK}" PAST_LOG_PATH = "logs/fail2ban.log" current_log = ti.xcom_pull(task_ids="get_current_log" ) current_log = current_log["log" ] try : with open (PAST_LOG_PATH, "r" ) as f: past_log = f.readlines() except : past_log = [] length_past_log, length_current_log = len (past_log), len (current_log) if length_past_log < length_current_log: with open (PAST_LOG_PATH, "w" ) as f: f.writelines(current_log) for cl in current_log[length_past_log:]: response = _send_discord_message(DISCORD_WEBHOOK, "```\n" + cl + "```" ) if not response.status_code == 204 : _send_discord_message( DISCORD_WEBHOOK, f"DISCORD WEBHOOK ERROR\n\tRESPONSE: {response.status_code} " , ) raise Exception( f"DISCORD WEBHOOK ERROR\n\tRESPONSE: {response.status_code} " ) time.sleep(1 ) elif length_past_log > length_current_log: response = _send_discord_message( DISCORD_WEBHOOK, "ERROR: THE PAST LOG IS LONGER THAN CURRENT LOG" ) if not response.status_code == 204 : _send_discord_message( DISCORD_WEBHOOK, f"DISCORD WEBHOOK ERROR\n\tRESPONSE: {response.status_code} " , ) raise Exception( f"DISCORD WEBHOOK ERROR\n\tRESPONSE: {response.status_code} " ) @dag( dag_id="Check-Jail" , start_date=airflow.utils.dates.days_ago(0 schedule_interval="@hourly" , max_active_runs=1 , catchup=False , def jail (): get_current_log = KubernetesPodOperator( task_id="get_current_log" , name="get_current_log" , image="airflow-get-current-log:v1.0" , do_xcom_push=True , volumes=[volume_config], volume_mounts=[volume_mount], ) check_jail = PythonOperator(task_id="check_jail" , python_callable=_check_jail,) get_current_log >> check_jail DAG = jail()
다 하고나니 아래와 같은 방법이 있었다…
허무한 결말 ~
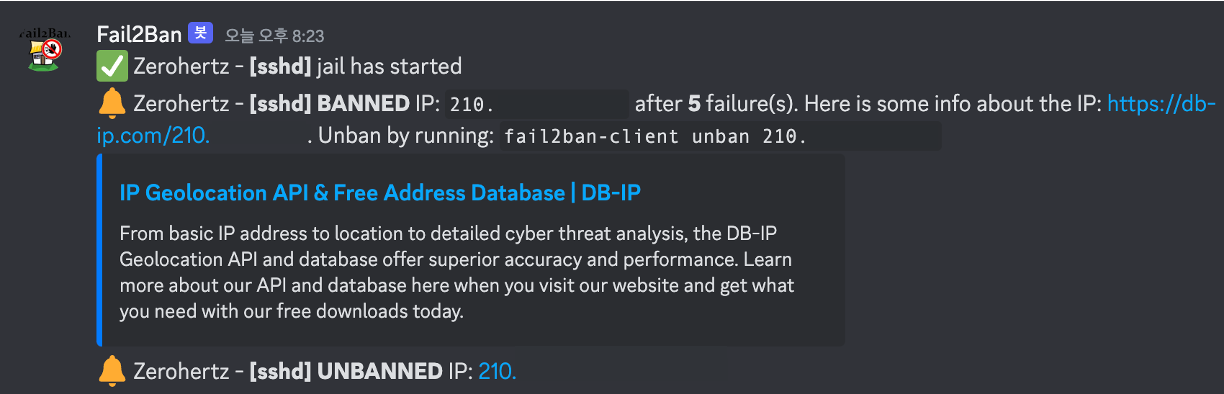
Adding ban/unban notifications from Fail2Ban to Discord! Logging Fail2Ban to Discord
/etc/fail2ban/jail.local (Discord) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [DEFAULT] findtime = 1d maxretry = 5 bantime = 1w backend = systemd ignoreip = 127.0.0.1/8 192.168.0.0/24 [sshd] enabled = true action = discord_notifications iptables-allports port = ${SSH_PORT} logpath = %(sshd_log)s backend = %(sshd_backend)s
/etc/fail2ban/action.d/discord_notifications.conf (Discord) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 [Definition] actionstart = curl -X POST "<webhook>" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"username": "Fail2Ban", "content":":white_check_mark: <hostname> - **[<name>]** jail has started"}' actionstop = curl -X POST "<webhook>" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"username": "Fail2Ban", "content":":no_entry: <hostname> - **[<name>]** jail has been stopped"}' actionban = curl -X POST "<webhook>" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"username":"Fail2Ban", "content":":bell: <hostname> - **[<name>]** **BANNED** IP: `<ip>` after **<failures>** failure(s). Here is some info about the IP: https://db-ip.com/<ip>. Unban by running: `fail2ban-client unban <ip>`"}' actionunban = curl -X POST "<webhook>" \ -H "Content-Type: application/json" \ -d '{"username":"Fail2Ban", "content":":bell: <hostname> - **[<name>]** **UNBANNED** IP: [<ip>](https://db-ip.com/<ip>)"}' [Init] name = default webhook = ${WEBHOOK} hostname = ${HOSTNAME}
심지어 대략적인 위치 정보도 제공하는 사이트를 링크해준다…
/etc/fail2ban/jail.local (Slack) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 [DEFAULT] findtime = 1d maxretry = 5 bantime = 1w backend = systemd ignoreip = 127.0.0.1/8 192.168.0.0/24 [sshd] enabled = true action = slack_notifications iptables-allports port = ${SSH_PORT} logpath = %(sshd_log)s backend = %(sshd_backend)s
/etc/fail2ban/action.d/slack_notifications.conf (Slack) 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 [Definition] actionstart = curl -X POST https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage \ -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \ -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d '{ "channel": "zerohertz", "text": ":white_check_mark: <hostname> - **[<name>]** jail has started", "username": "Fail2Ban", "icon_emoji": ":bank:", }' actionstop = curl -X POST https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage \ -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \ -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d '{ "channel": "zerohertz", "text": ":no_entry: <hostname> - **[<name>]** jail has been stopped", "username": "Fail2Ban", "icon_emoji": ":bank:", }' actionban = curl -X POST https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage \ -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \ -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d '{ "channel": "zerohertz", "text": ":bell: <hostname> - **[<name>]** **BANNED** IP: `<ip>` after **<failures>** failure(s). Here is some info about the IP: https://db-ip.com/<ip>. Unban by running: `fail2ban-client unban <ip>`", "username": "Fail2Ban", "icon_emoji": ":bank:", }' actionunban = curl -X POST https://slack.com/api/chat.postMessage \ -H "Authorization: Bearer <token>" \ -H "Content-type: application/json" \ -d '{ "channel": "zerohertz", "text": ":bell: <hostname> - **[<name>]** **UNBANNED** IP: [<ip>](https://db-ip.com/<ip>)", "username": "Fail2Ban", "icon_emoji": ":bank:", }' [Init] name = default token = ${SLACK_BOT_TOKEN} hostname = Zerohertz